The Explosion of Space Discoveries
Are you prepared for some awe-inspiring astronomical discoveries (which you might not usually be privy to)? The James Webb space telescope has elevated the realm of space exploration, providing us with a more profound comprehension of the cosmos. Although many such advancements garner media coverage, numerous space anomalies are often overlooked. Today, these lesser-known facets will be brought to your attention.
From exoplanets to distant star systems, get a bowl of popcorn, put on your space hat, and let’s launch into orbit with these 25 min-blowing space discoveries you’ve never heard of!

Detection of Gravitational Waves
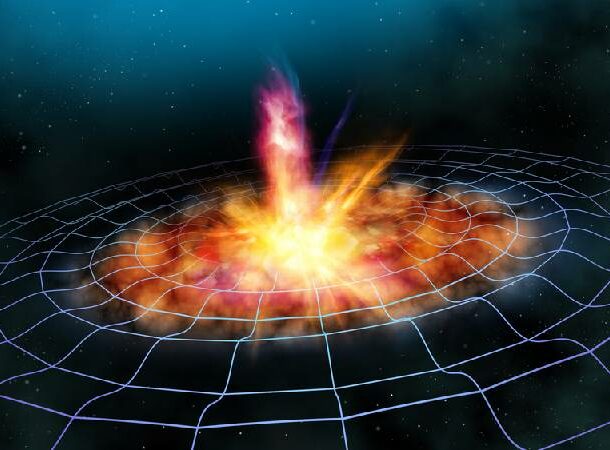
Let’s kick this list off with a ripple in space-time, shall we?
As a bit of background, when a star runs out of energy, it collapses in on itself. This creates either a black hole or a neutron star.
According to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, if an object has mass, it exerts gravity. The curvature of space-time is distorted by gravity.
In 2017, scientists recorded two neutron stars crashing into each other. Was there a big boom? Probably not, because of the absence of sound waves in space, but there were gravitational waves.
The powerful impact of the two stars colliding created gravitational waves that caused a ripple in space-time.
Dark matter

By now, you’ve probably at least heard the term “dark matter.” If you’re not sure what that really is, don’t worry, because neither are scientists.
What they have discovered, though, is that star distribution and the movement of galaxies don’t behave the way they “should” if space was made up of “normal” matter—even if they play around with alternative theories of gravity.
It’s extra proof that dark matter exists, but we don’t know what it is.
Related: 25 Most Bizarre Galaxies In The Universe
Spacex Space Crafts
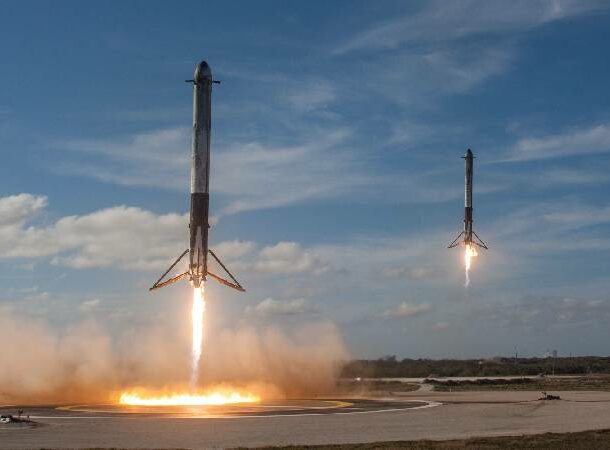

No, it’s not a new planet or galaxy, but SpaceX’s innovative spacecraft are changing the way we explore space. With the Falcon 9, SpaceX has changed the game completely. What’s the big deal? a multi-mission and multi-use spacecraft. It’s already changing areas like communication via satellite (Starlink).
Imagine how many more missions can be completed now… not to mention the ability to send people that are not astronauts into space. Maybe we will go to Mars after all.
Related: 25 Air And Space Crafts That Helped Shape History
First Image of Black Hole
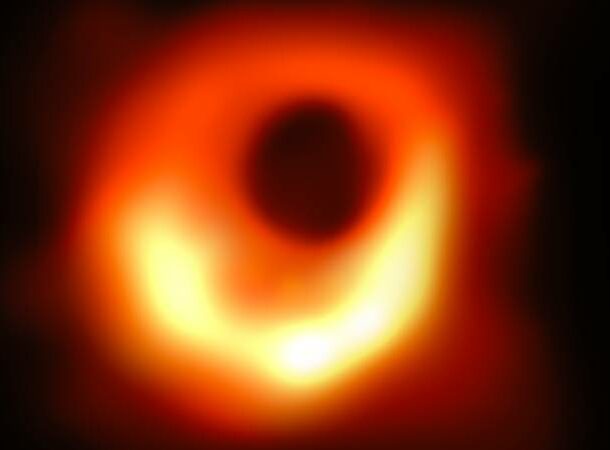

Do you know when we had the first image of a black hole—the actual photographic proof of their existence? While you’ve been hearing about them since grade school, scientists didn’t get a clear picture until 2019 with the event horizon telescope. This specific black hole is in the heart of the M87 galaxy, 55 million light years away. Prior to this, scientists thought they were simply “unseeable”.
Related: 20 Black Hole Facts To Blow Your Mind
Gamma Ray Bubbles
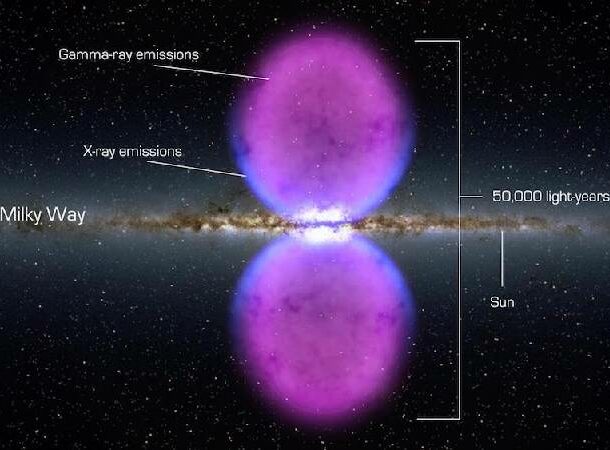
Black holes are pretty impressive by themselves, but hovering above Sagittarius in the Milky Way’s nucleus are two expanding bubbles of gamma rays. The discovery was made in 2010, but we aren’t sure yet of their origin. The bubbles touch at the galaxy’s center, forming a wide hourglass shape.
The Search For a Sister Planet & Super-Earth

The search for another habitable planet has been ongoing for a long time. Our planet is uniquely suited to support life here, and there hasn’t been a match yet. The closest options? Exoplanet Ross 128b, discovered in 2017, and the super-Earth-like planet called Speculoos-2c, or LP 890-9c, discovered recently in 2022
Speculoos-2c is farther away from us than Ross128b, but it is 40% bigger than the earth, and while it orbits closer to its sun, its sun is six times smaller and half the temperature.
Synestia Theory

So, this is just a theory, but… the earth was once a donut. Not a boston crème or chocolate sprinkled, but a synestia.
A synestia is a short-lived, donut-shaped, hot mass. These masses are thought to result from the collision of two planet-sized bodies. The theory is that the earth was once a synestia, about 4.5 billion years ago.
Magnetic feeding fields

Magnetic fields in the Cygnus galaxy are acting as a sort of net for material from space. That might make you go, “meh,” but what’s cool about this magnetic field is that it’s created the perfect way to “feed” and power the hungry supermassive black hole at the galaxy’s center.
Black Hole Magnetic Field

Speaking of blackholes and magnetic fields… typically, blackholes pull material into them if they get too close, but the central black hole in the milky way galaxy has magnetic fields surrounding it in such a way that directs material *around* the hole instead of into it.
Related: 25 Crazy Facts About Black Holes
A Booze Comet
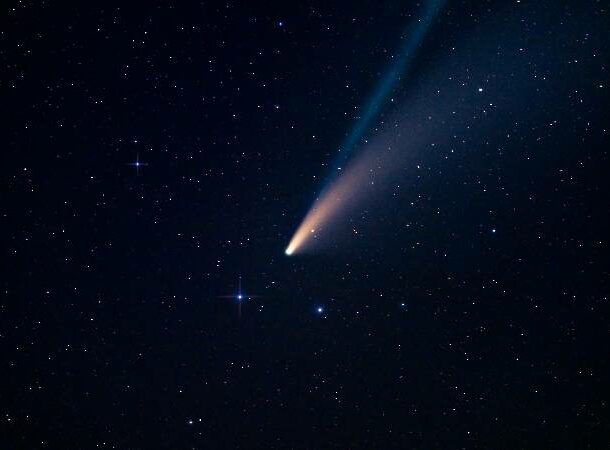

Okay, so it’s not what your local bar has on tap, but Comet Lovejoy left a trail of ethyl alcohol, which is something booze has in it.
A team of scientists at the Paris Observatory also found evidence of 21 organic molecules, including a type of sugar (also in booze).
The molecules found support the theory that comets might have contained life-creating components at one point.
Space bubbles
 Credit: MIT
Credit: MIT In the Orion nebula, there is a newborn star that is giving itself some extra space (pun intended). Stellar wind from this newborn star is blowing around it, preventing further seed material from turning into more new stars.
This sheds new light on how stars are formed. It’s thought that new stars are formed from exploding stars called supernovas. However, now it’s thought that perhaps infant stars generate this wind to blow away this seed material.
Voyager’s Continued Discoveries

Okay, so Falcon 9 is an awesome spacecraft. However, before SpaceX and all its innovations, there were Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 became the first spacecraft to reach interstellar space in 2012. (Interstellar space is the space between the star systems in a galaxy.)
Voyager is still sending information back from an uncharted region of the universe.
Spinning Black Holes

In 2015, there was a disruption in distant space thought to be a supernova. It produced a light 20 times brighter than the entire production of the Milky Way.
However, in 2016, a team of researchers published a paper explaining that it was a dying star pulled into a spinning supermassive black hole. These spinning black holes don’t only pull in things at their event horizon; they also suck in outside celestial bodies.
Interstellar object
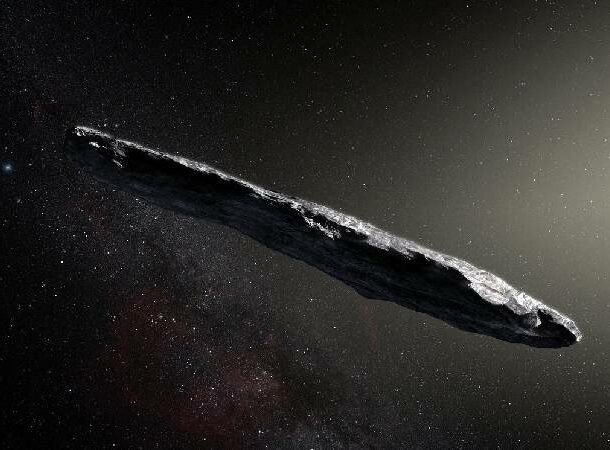

An interstellar object is one that is not tied down by the gravitational pull of a star.
While comets, asteroids, and rogue planets all meet this definition, the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope in Hawaii spotted a different type of interstellar object in our galaxy roughly the size of a football field, if not bigger.
It’s nicknamed “Oumuamua” (roughly translated to “scout”) and is the first one to be discovered passing through our galaxy. Scientists believe it came from a planet outside our solar system.
Epsilon Eridani
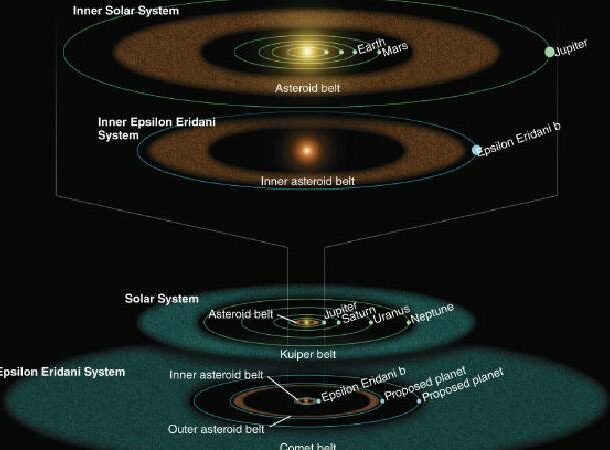 Image credit: NASA / JPL / Caltech / R. Hurt, SSC.
Image credit: NASA / JPL / Caltech / R. Hurt, SSC. In 2017, scientists discovered a planetary system that has a strikingly similar structure to our own. The system even surrounds a star similar to our early sun.
Fun fact: Epsilon Eridian is the location of the fictional Babylon 5 space station from the TV series Babylon 5.
Ice volcano
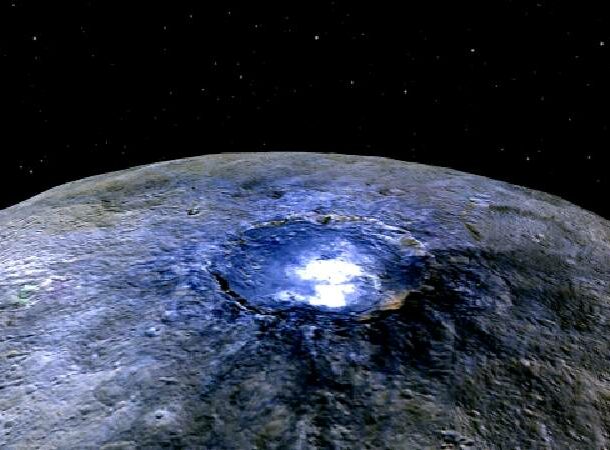

Volcanoes here on planet Earth release super-hot molten rock. Volcanoes on other planets don’t necessarily work the same way.
In 2015, NASA’s Dawn mission found a volcanic mountain on the dwarf planet Ceres. This mountain is thought to have been formed by a cryovolcano that released freezing salt water mixed with mud.
Gaia mapping
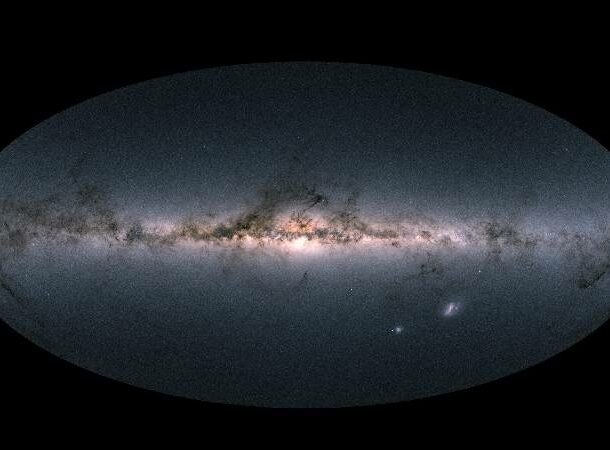

Launched in 2013, satellite Gaia has the purpose of taking distance measurements for more than a billion stars in the Milky Way, along with velocity data for more than 150 million stars.
The results? The mapping of 1.7 billion stars in our galaxy This helps scientists study how our galaxy formed, how it is now, how quickly it’s expanding, and a lot more.
Asteroid tracking with James Webb
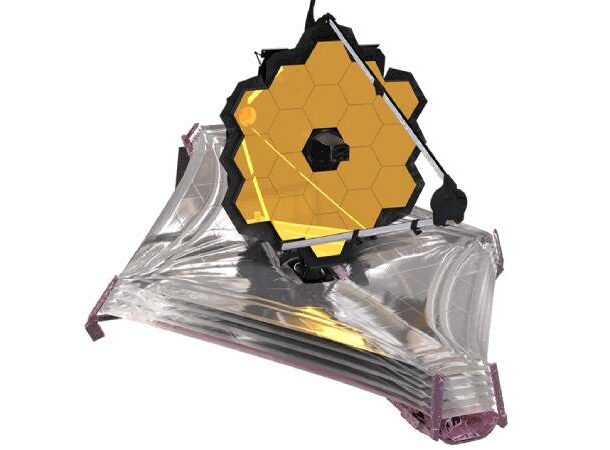

While scientists have been able to see asteroids, until recently, they had been unable to track a moving asteroid. With the james webb space telescope, we can now keep track of these objects and more to see where and how they are moving. Pretty cool,
Wind in Cigar Galaxy
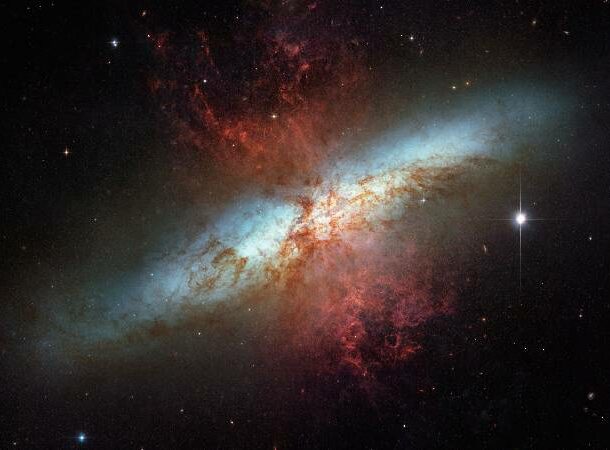 Image Credits: NASA
Image Credits: NASA The Cigar Galaxy is known for the incredible speed at which it produces new stars—10 times faster than the Milky Way.
In the center of the galaxy is a powerful wind aligned with a magnetic field. This wind-driven magnetic field transports a mass of gas and dust equal to the mass of 50 or 60 million suns!
Related: 25 Almost Unbelievable Facts About the Milky Way
Early universe

What is the oldest or earliest universe? Well previously it was thought to be Glass-z13 estimated to be 300,000,000 years after the big bang However, the James Webb found one, by accident mind you, that’s older – ., estimated to be 235 million years after the big bang.
Water on The Moon
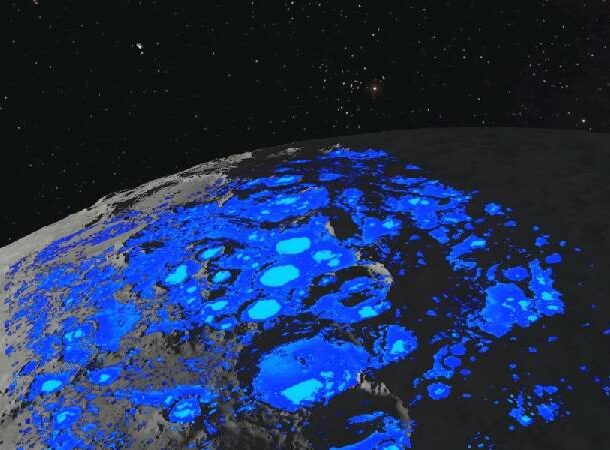
In 2018, ice was discovered on the north and south poles of the moon, but now there’s more proof. The stratospheric observatory for infrared astronomy discovered the wavelength for water molecules in the Clavice crater.
Tsunamis & Ice Deposits On Mars
 Image Credit: NASA
Image Credit: NASA Mars has always been a planet worthy of speculation and exploration; who knows, we may even live there one day. There have been a couple key Martian discoveries in the past decade. In 2016, an ice layer bigger than the state of New Mexico was discovered below 3 to 33 feet of soil. Also below the surface of Mars, Shorelines that were created by two mega-tsunami events It’s looking more and more possible that Mars once had an ocean below its surface.
Jupiter and its moons
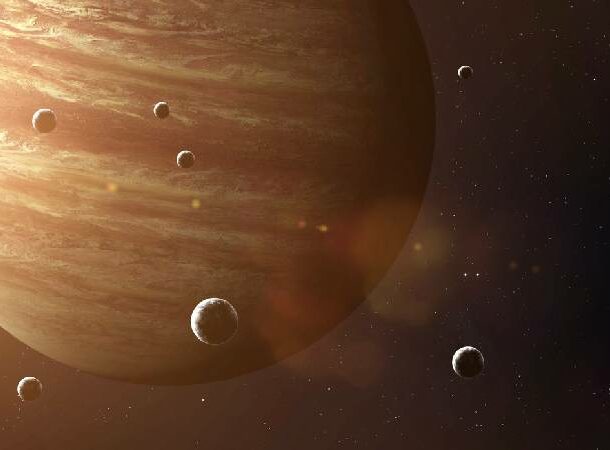

Jupiter’s gravitational pull has attracted a large number of moons, ranging in size from the planet Mercury to a standard sports arena.The strange part? We’re not 100% sure how many moons Jupiter has. The current count is 83, with 20 more waiting for confirmation of discovery and official names.
Thanks to the James Webb Space Telescope, we are also learning a lot of other things about Jupiter, such as areas of higher and lower altitude.
Exoplanet atmosphere

An exoplanet is a planet outside the solar system, and thanks to advancements in technology, we know that they are common in the Milky Way and likely throughout the universe.
Another discovery from the James Webb Space Telescope is the chemical and molecular makeup of one of these exoplanets.
Wasp-39b, also known as “hot Saturn,” has chemicals such as potassium, sodium, water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and sulfur dioxide in its atmosphere.
New galaxies
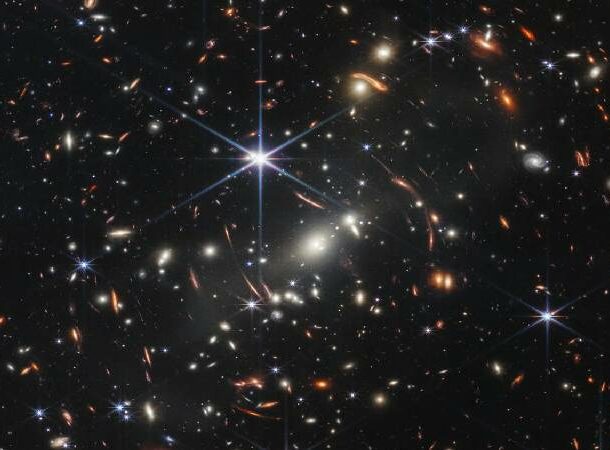 Image Credit: NASA
Image Credit: NASA Thanks to the James Webb space telescope, what’s really mind-blowing is how ginormous the universe is. Researchers have now identified 55 distant galaxies, and 44 of those galaxies have never been observed before.



























