There is no arguing the fact that outer space is home to some of the most captivating phenomena and entities ever seen by mankind. In the past, we could only speculate about what existed beyond our planet, but modern advancements in technology, telescopes, and other astronomical equipment now offer us a good grasp of what the surrounding universe actually looks like. You’re on the verge of experiencing it yourself – images taken from NASA’s telescopes, sourced from thousands and millions of light-years away, are beautifully captivating. Whether it’s breathtaking photos of nebulas and gas clouds, or the iconic Pillars of Creation, these 25 Space Images Will Surely Leave You Awestruck.

This spectacular picture features cosmic pairing of the star Hen 2-427 and the nebula M1-67 which surrounds it. The nebula M1-67 is estimated to be no more than 10,000 years old — just a baby in astronomical terms — but it makes truly beautiful and magnificent sight.
 Source and image: nasa.gov
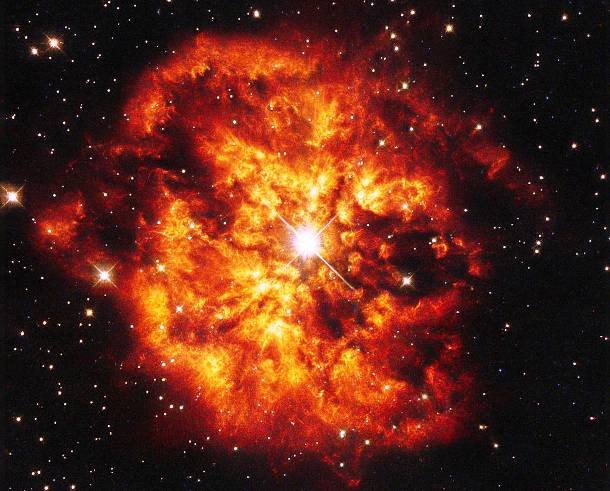
Source and image: nasa.gov Final moments of a dying star. While a star´s death may only last mere moments on a cosmological timescale, it is still quite lengthy by our standards, lasting tens of thousands of years. After a star has burned out its fuel supply, its remnants (depending on the mass during its lifetime) can take one of three forms: white and black dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes.
 Source and image: nasa.gov
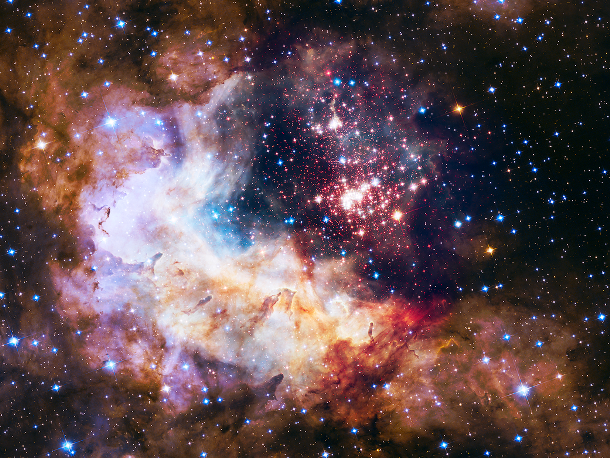
Source and image: nasa.gov What looks like a giant celestial firework show is actually a cluster of young stars flaring to life. Stellar evolution starts with the gravitational collapse of a giant molecular cloud. Typical giant molecular clouds are roughly 100 light-years across and contain up to 6,000,000 solar masses (1.2×1037 kg).
 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Spanning about 10 light years, the Crab Nebula is the result of a supernova noted by Earth-bound chroniclers in 1054 A.D. Spanning about 10 light-years, the nebula contains a pulsar - a neutron star as massive as the Sun but with only the size of a small town.
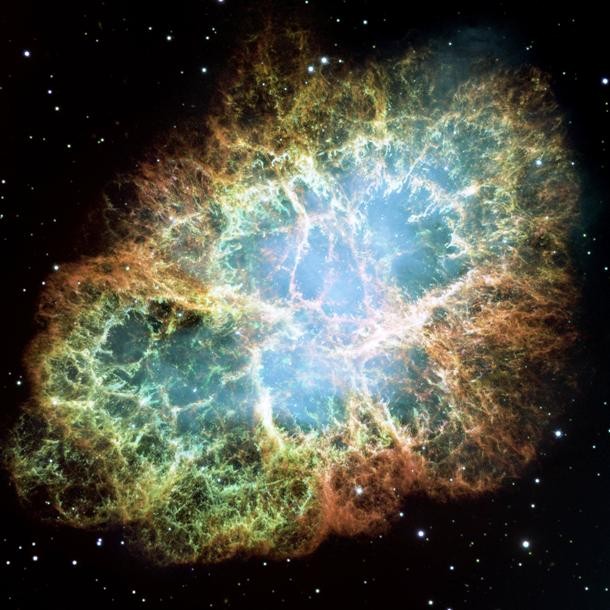 Source and image: nasa.gov
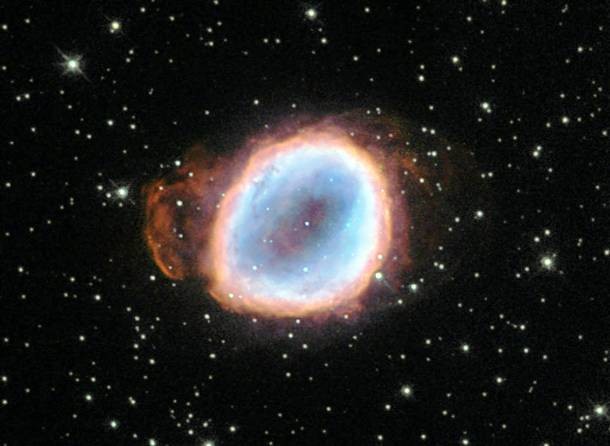
Source and image: nasa.gov This is the center of Messier 22, an elliptical globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. Messier 22 is one of about 150 globular clusters in the Milky Way and at just 10,000 light-years away, it is also one of the closest to Earth. It was discovered in 1665 by Abraham Ihle, making it one of the first globulars ever discovered.
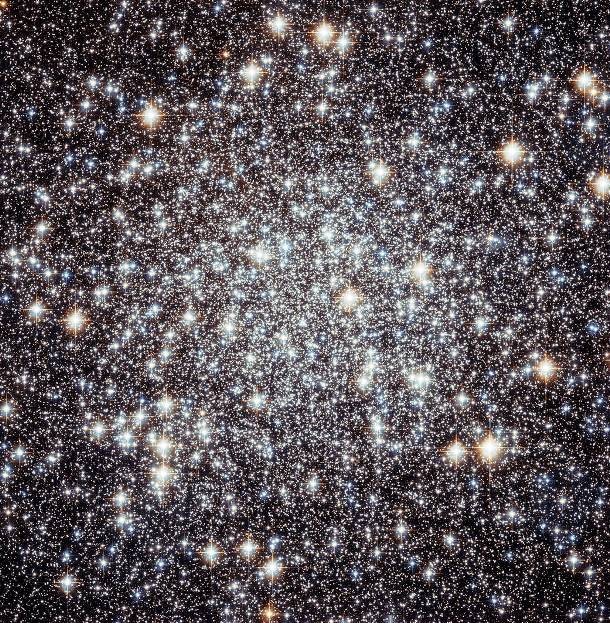 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Found 5,000 light years away, the Bubbly Nebula is a planetary nebula appearing in the large but faint constellation Camelopardalis. Discovered by William Herschel in 1787, the nebula is just under 5,000 light-years away from us. Astronomers have modeled the three-dimensional structure of the nebula, finding it to be a cloud shaped as an irregular ellipsoid filled with bumpy and bubbly regions.
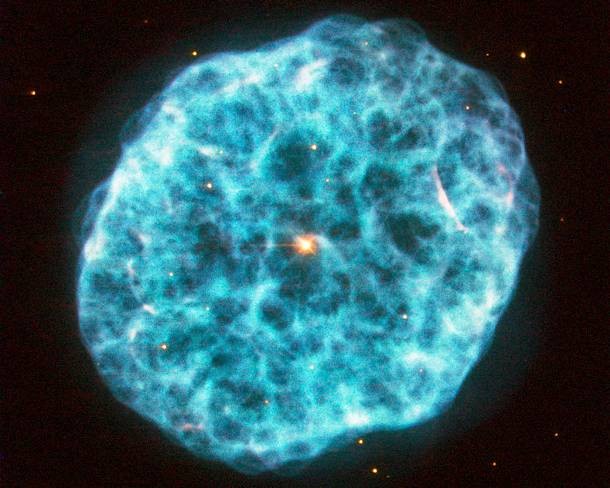 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Located some 10 billion light years away, this enormous water vapor cloud is estimated to hold up to 140 trillion times the mass of water found in all Earth´s oceans. The water surrounds a huge, feeding black hole, called quasar APM 08279+5255 that was discovered in 1998.
 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov This bizarre dot resembling an eye can be found on Jupiter, the biggest planet of the Solar System. Known as the Great Red Spot, it is a giant storm that is known to have existed since at least the 17th century when it was first seen by telescope.
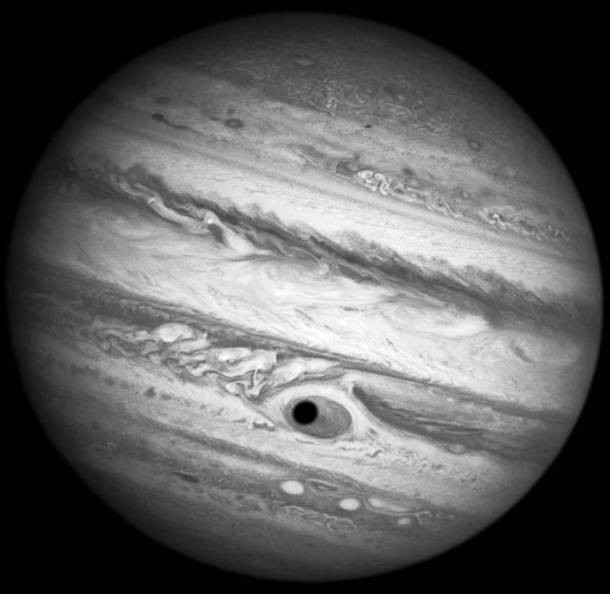 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov What looks like a giant smiling face is the center of the galaxy cluster SDSS J1038+4849. Galaxy clusters are the most massive structures in the Universe and exert such a powerful gravitational pull that they warp spacetime around them and act as cosmic lenses which can magnify, distort and bend the light behind them.
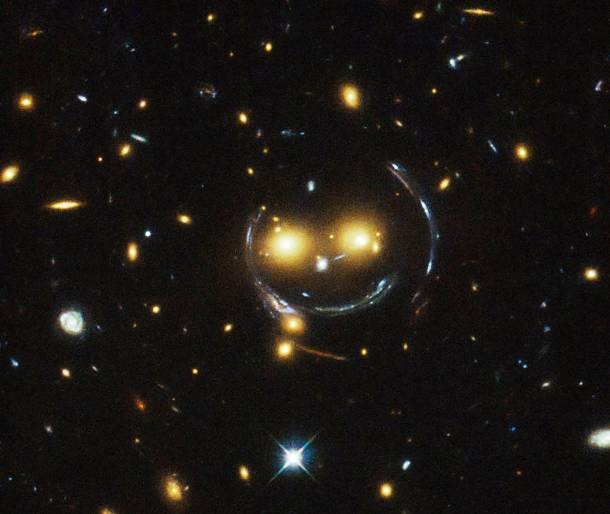 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Located in the nebula-rich constellation Sagittarius, the Trifid Nebula is easy to find even with a small telescope. This spectacular false-color view is courtesy of the Spitzer Space Telescope. Astronomers have used the Spitzer infrared image data to count newborn and embryonic stars that otherwise lie hidden in the natal dust and glowing clouds of this intriguing stellar nursery.
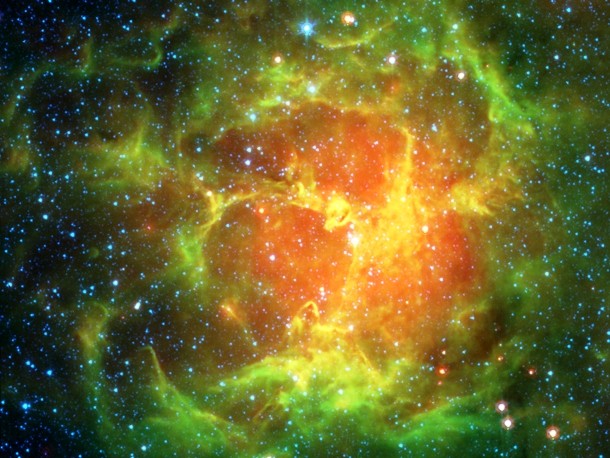 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov One of the most iconic space images ever, this picture was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2014. It features the so-called Pillars of Creation, huge gas columns found in the Eagle Nebula. The image shows that the very ends of the pillars are dense knots of dust and gas. They shadow the gas below them, keeping the gas cool and creating the long, column-like structures.
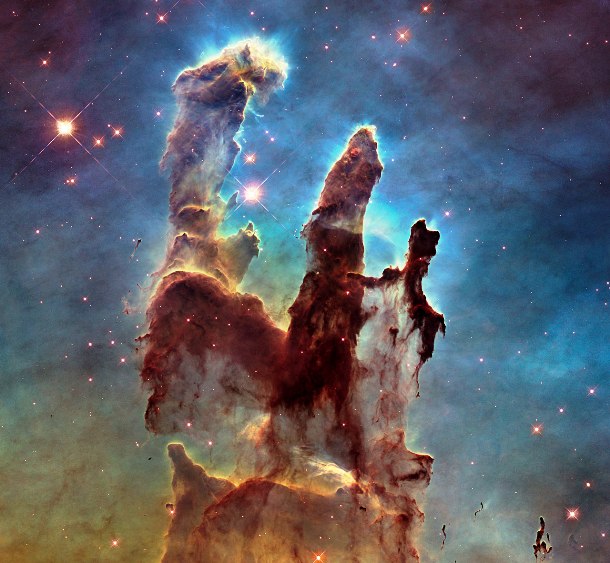 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov This colorful mosaic of a small part of the Monkey Head Nebula unveils a collection of carved knots of gas and dust silhouetted against glowing gas. Located some 6,400 light-years away, the cloud is sculpted by ultraviolet light eating into the cool hydrogen gas.
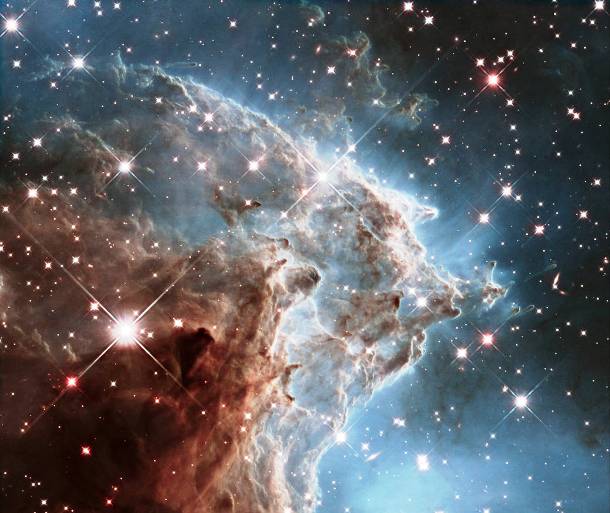 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Resembling a human head, the Eskimo Nebula was discovered by a British astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The Eskimo Nebula is clearly a planetary nebula, and the gas seen above composed the outer layers of a sun-like star only 10,000 years ago.
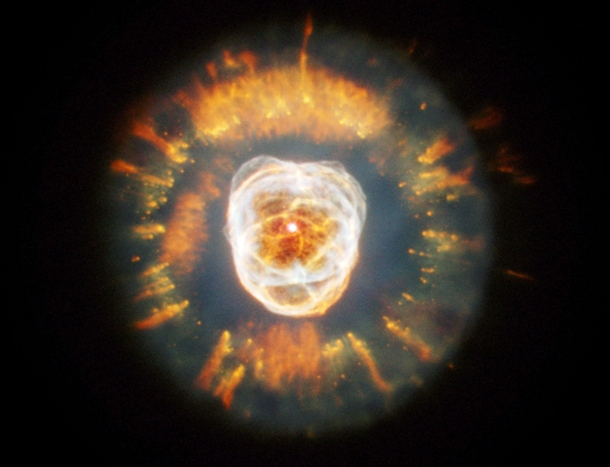 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov The sharpest image of the Antennae Galaxies that has ever been taken. The galaxies — also known as NGC 4038 and NGC 4039 — are locked in a deadly embrace. Once normal, sedate spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, the pair have spent the past few hundred million years sparring with one another.
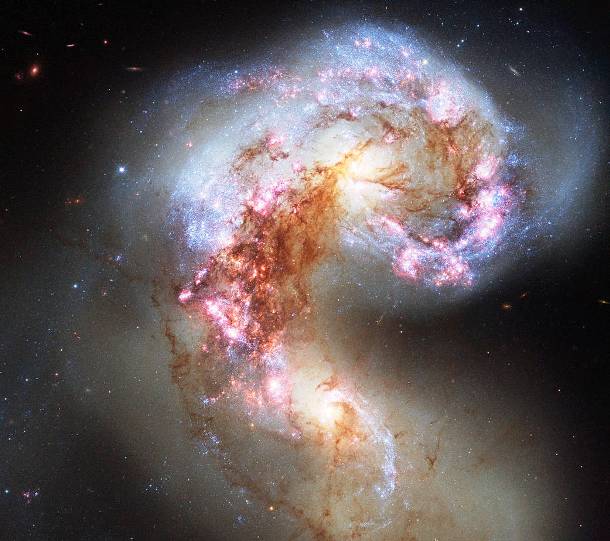 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov This is a composite image of Cassiopeia A supernova remnant, one of the most famous cosmic objects. Discovered in 1948 by Martin Ryle and Francis Graham-Smith, astronomers at Cambridge, it is a supernova remnant in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz.
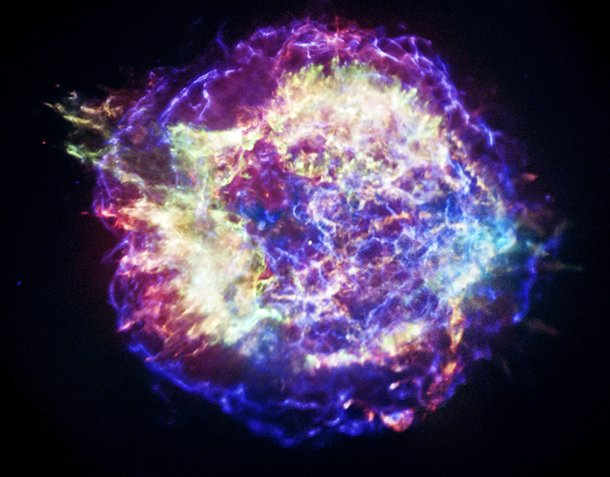 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov In January 2002, star V838 Mon's outer surface suddenly expanded, which temporarily made it the brightest star in the entire Milky Way Galaxy. Then, just as suddenly, it faded. V838 Mon lies about 20,000 light years away toward the constellation of the Inicorn (Monoceros), while the light echo above spans about six light years in diameter.
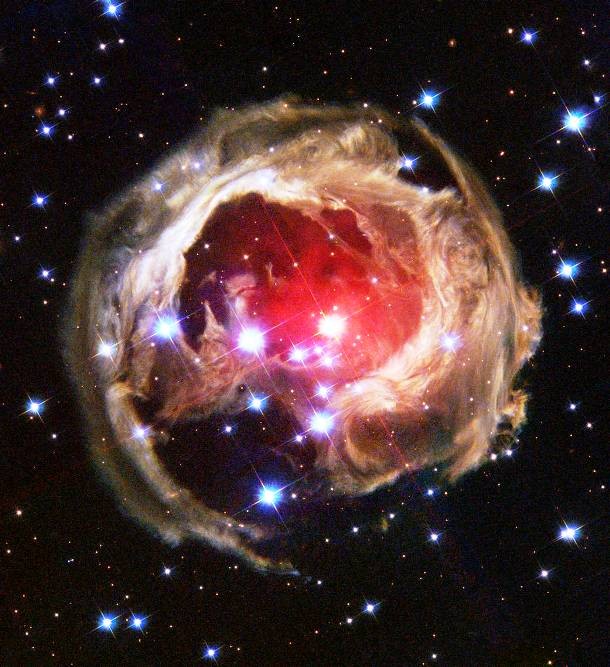 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Easily recognizable thanks to its “wings” covering over 3 light years, the Butterfly Nebula lies about 4,000 light years away in the constellation Scorpion. This sharp and colorful close-up of the dying star's nebula was recorded in 2009 by the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Camera 3, installed during the final shuttle servicing mission.
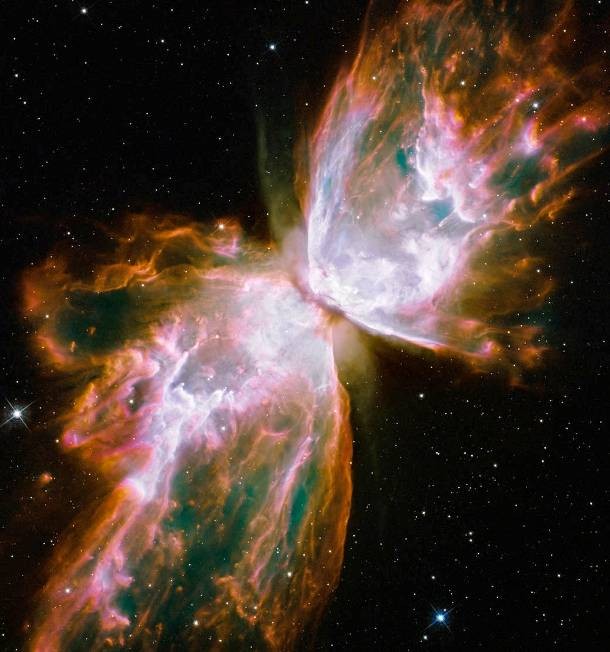 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Resembling a hat, this is the Sombrero Galaxy. The spectacular dust rings harbor many younger and brighter stars, and the center of the galaxy is thought to house a large black hole. Fifty million-year-old light from the Sombrero Galaxy can be seen with a small telescope towards the constellation of Virgo.
 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Traveling at speeds of 900 miles (1,448 km) per second, this coronal mass ejection erupted into space and connected with Earth’s magnetosphere to cause an aurora. Coronal mass ejections are often associated with other forms of solar activity, most notably solar flares or filament eruptions, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established.
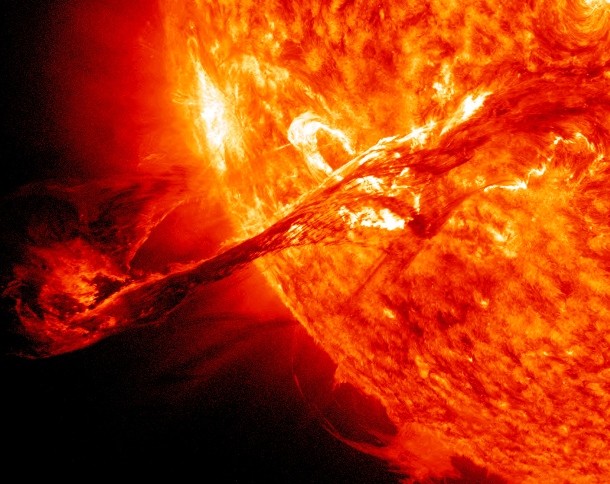 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Taken in September 2011, this picture shows an aurora crossing over the southern Indian Ocean. While auroras usually occur near the poles, this one appeared at lower latitudes due to a geomagnetic storm. The storm was a moderate one, rated with what's called a KP index of 6 on a scale that goes from 0 to 9, caused by just a glancing blow from the coronal mass ejection.
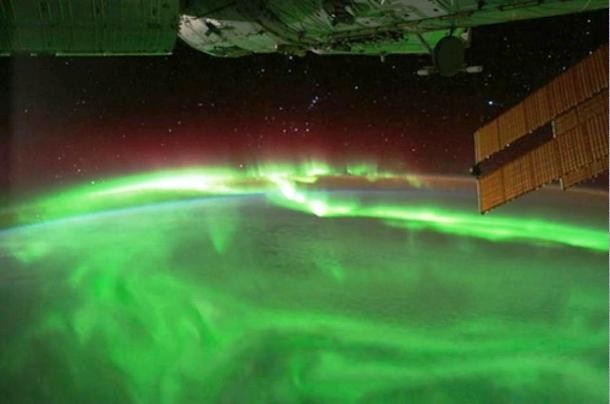 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov One of the most popular targets of both professional and amateur astronomers, the iconic Horsehead Nebula is just a tiny part of much larger and complex Orion Nebula. The horse-head feature is dark because it is really an opaque dust cloud that lies in front of the bright red emission nebula.
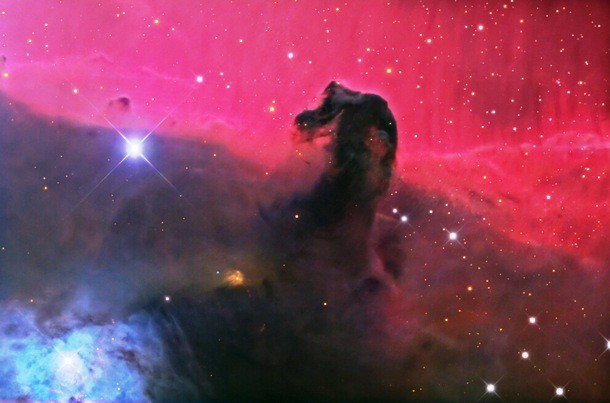 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov This is the most detailed visible-light image of a narrow, dusty ring around the star Fomalhaut, one of the brightest stars in the sky. Lying 25 light years away, Fomalhaut is the brightest star in the constellation Piscis Austrinus.
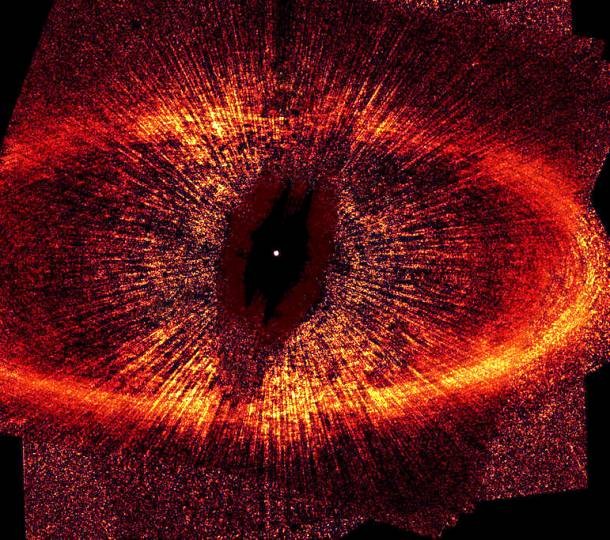 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov In early 2002, the Hubble Space Telescope captured a unique phenomenon known as the light echo around the star V838 Monocerotis as it suddenly brightened for several weeks. Variable star V838 Monocerotis lies near the edge of our Milky Way Galaxy, about 20,000 light-years from the Sun.
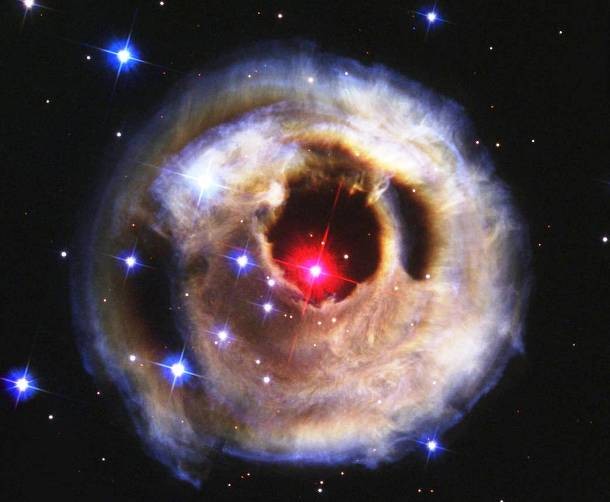 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov At approximately 2.5 million light years away, the Andromeda galaxy is our Milky Way's largest galactic neighbor. Despite earlier findings that suggested that the Milky Way contains more dark matter and could be the largest in the grouping, the 2006 observations by the Spitzer Space Telescope revealed that Andromeda contains one trillion stars, at least twice the number of stars in the Milky Way.
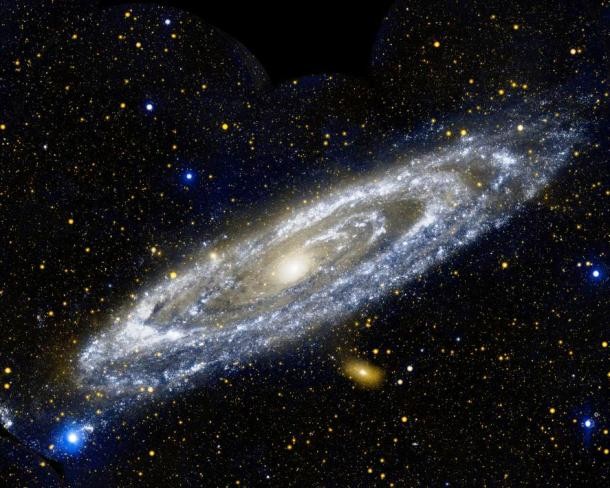 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov Located some 200,000 light years from Earth, the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way ablaze with star-forming regions, floats in space. From the Tarantula Nebula, the brightest stellar nursery in our cosmic neighborhood, to the Bean Nebula, the small and irregular galaxy is scattered with glowing nebulae, the most noticeable sign that new stars are being born.
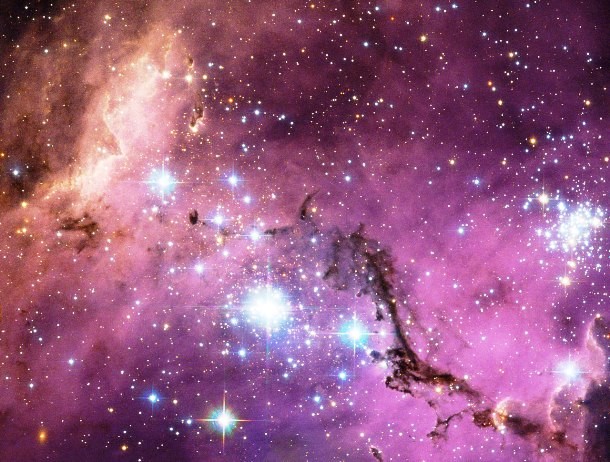 Source and image: nasa.gov
Source and image: nasa.gov 


























