Isn’t the concept of travelling in space just absolutely fascinating? Surely, everyone has questioned what it would really feel like to take a walk on the moon.
However, there are some facts that might make you reconsider your perspective. From the dreadful repercussions of losing your total body orientation to the failure of some of our best technology to adapt effectively to outer space, you may have yet to anticipate many aspects of space travel.
Here are 25 SCARY But True Space Facts.

The Universe Could Rip Itself Apart
 https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/expanding-universe-slows-then-speeds/
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/expanding-universe-slows-then-speeds/ By now, we all know that the universe is expanding. Although its nature is still a mystery, scientists agree that dark energy might be behind it all.
Now, here comes the scary part. Several scientists believe the universe’s expansion could eventually tear the universe apart, just like the Enterprise at Warp Factor Nine.
One of the most frightening aspects of this idea is that while most end-of-world scenarios occur after the human race is long gone and nothing is left, the Big Rip (that’s a catchy name for the end of the world) is scheduled to take place in about 16 billion years – when planets (and possibly life) could still exist. This universe-wide catastrophe could either burn everything and everyone alive, rip them apart, or feed them to the celestial space squids that dwell among universes. I mean, who knows – they could be there. But it will almost certainly be an infinitely more grisly demise than anyone expected.
Moon Dust Will Kill You
 https://www.livescience.com/62590-moon-dust-bad-lungs-brain.html
https://www.livescience.com/62590-moon-dust-bad-lungs-brain.html Just about everything in outer space will kill you. Yet, one of NASA’s biggest headaches isn’t a lack of oxygen or a punctured suit but moon dust. The particles cling to everything, including suits, and a good stomp of the feet would have sufficed if we were looking at the dust here on Earth, but moon dust can kill you.
In 2018, scientists confirmed that fact. Unlike the powdery dust down here, the lunar particles are razor-sharp, never degrade, and consist mostly of meteorite fragments. When scientists exposed the lunar dust to human cells in their laboratories, it sliced and demolished nearly 90% of lung and brain tissue in less than 24 hours. The cells that survived suffered such extensive DNA damage that they were at risk of developing malignancies and neurodegenerative disorders.
The Gigantic Rogue Black Hole
 https://www.express.co.uk/news/science/1156927/black-hole-big-as-jupiter-milky-way-space-news
https://www.express.co.uk/news/science/1156927/black-hole-big-as-jupiter-milky-way-space-news When it comes to things that really shouldn’t go rogue – a black hole is probably right there at the top.
A black hole is an area of space with a gravitational field so strong that even light cannot escape it. It literally gobbles up everything that dares wander into its gravitational field, so they should be avoided, to put it mildly.
It becomes a problem, however, if one of them decides the stationary life is not for them.
Like everything else in our galaxy, black holes can find their own movement trajectories, and if that happens, they move at breakneck speed, devouring everything in their path.
Which is exactly what is going on in the Milky Way.black hole the size of Jupiter is currently tearing its way through the galaxy. And while we are safe from it at the moment, it’s going to be a different situation in the Earth’s distant future.
What Would Happen To Your Body Without A Suit
 https://www.cnet.com/news/what-happens-to-the-unprotected-human-body-in-space/
https://www.cnet.com/news/what-happens-to-the-unprotected-human-body-in-space/ I know we’ve all wondered about this, so let’s put it out there. What would actually happen to your body if you ever get sucked out of your spaceship without wearing your space suit?
Well, you will deplete all of the oxygen in your blood in about 15 seconds. If you don’t hold your breath, that is. If you do, the remaining air in your lungs will force them to expand, rupturing them and allowing air into your indispensable circulatory system.
The first thing you’ll want to do if you trip out of the airlock like a badly dressed Syfy henchman is exhale. I know it seems absurd, but it’s not like diving underwater.
Speaking of water, given the lack of pressure, the water in your tissues will begin to vaporize after about ten seconds. You will also experience a burning sensation on your tongue, sunburned skin, and symptoms of decompression sickness. You won’t freeze right away, and you won’t decompose – so we could leave you up there or reel you back in. Either way, being a floating icicle in space doesn’t sound like the worst way to go.
Extended Space Travel Can Change Your DNA
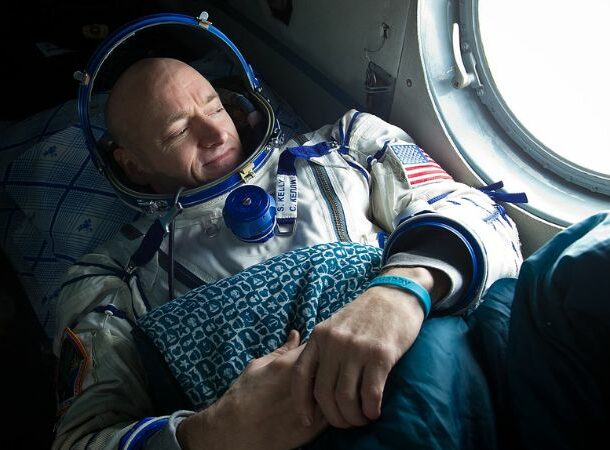 https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation-now/2018/03/15/space-genes-nasa-confirms-space-travel-changes-dna-perhaps-long-time/427402002/
https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation-now/2018/03/15/space-genes-nasa-confirms-space-travel-changes-dna-perhaps-long-time/427402002/ NASA has been analyzing the effects of long-term space travel on our DNA by studying identical twins – astronaut Mark Kelly and his brother Scott.
Scott went to the International Space Station, where he spent nearly a year without gravity. And, while Scott was in space, Mark carried out identical trials here on Earth, allowing the 84 scientists involved in the study to see how much microgravity conditions changed the human body.
Unsurprisingly, since our bodies were created to withstand Earth’s gravity and conditions, Scott went through significant changes that included:
- Reduced body mass
- Changes to his eye shape
- He developed an overactive immune system and
- He experienced changes to his chromosomes
Fortunately, once Scott returned to Earth, his body recovered (more or less).
Stars Can Come Back From The Dead
 https://www.eso.org/public/blog/a-star-is-born-again/#:~:text=Like anything in astronomy%2C the,short second lease of life.
https://www.eso.org/public/blog/a-star-is-born-again/#:~:text=Like anything in astronomy%2C the,short second lease of life. If The Lion King taught me anything, it’s that every living thing has to die at some point in the great big circle of life.
Now, you might recall that the death of a star is one of the most intriguing spectacles in the macrocosm. Every star visible in the heavens died long ago or will cease to exist in the years to come. That is the natural order of the world as we know it.
Unless it isn’t.
Scientists recently discovered that some stars die and then miraculously come back to life. And nobody knows why. In fact, the zombie stars (as we’ve come to know them) actually seem to have a revitalized sense of vigor.
Space Can Make You Nearsighted
 https://www.sciencealert.com/we-finally-know-why-astronauts-lose-their-vision-in-space-and-it-s-bad-news-for-mars-missions
https://www.sciencealert.com/we-finally-know-why-astronauts-lose-their-vision-in-space-and-it-s-bad-news-for-mars-missions As if changes to your DNA and immune system weren’t enough, an unidentified disorder has been affecting astronauts’ eyesight on the International Space Station, leading to untreatable nearsightedness that lasts months when they return to Earth.
The situation is so serious that more than half of astronauts have reported that their eyesight deteriorated after spending time in orbit. NASA believes that the condition – VIIP (visual impairment inter-cranial pressure syndrome) – is triggered by the lack of gravity in space.
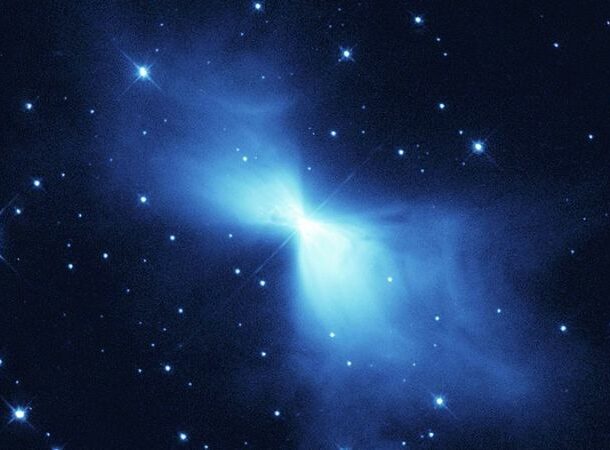
The Coldest Place In The Universe
 https://cosmosmagazine.com/space/astronomy/explainer-is-there-sound-in-space/#:~:text=No%2C there isn't sound in space.&text=This is because sound travels,to vibrate – so no sound.
https://cosmosmagazine.com/space/astronomy/explainer-is-there-sound-in-space/#:~:text=No%2C there isn't sound in space.&text=This is because sound travels,to vibrate – so no sound. The universe is a cold place. And while we know it’s cold, nobody is sure just how cold it can get. According to scientists, the Boomerang Nebula (a giant mass of gas and dust) is the absolute coldest place in our universe.
In fact, it’s so cold (-457.87F on average) that scientists have been trying to figure out what happened to it for a very long time and recently discovered a plausible reason for it.
They believe the nebula was expelled after two stars collided, causing the matter of one star to be discharged as a cold burst. While it’s still too far away to be dangerous, it’s the one place we should probably all agree not to visit if we ever figure out interstellar travel.
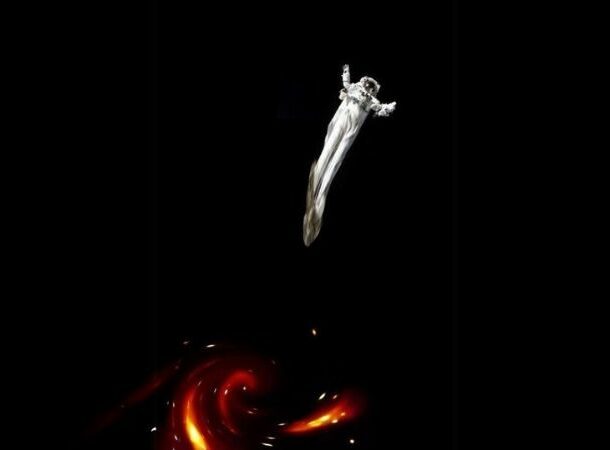
If You Fell Into A Black Hole, You Would Be Strung Out Into Spaghetti
 https://www.bbcearth.com/news/what-would-happen-if-you-fell-into-a-black-hole
https://www.bbcearth.com/news/what-would-happen-if-you-fell-into-a-black-hole While it has never been put to the test (for obvious reasons), scientists are convinced that if you go into the event horizon of a black hole, you are going to experience tidal forces caused by the massive gravity. Because of your body’s cohesive nature, you will be ripped apart.
A jump head-first into such a black hole would cause your head to be pulled so far from your feet that you would resemble spaghetti. The theory is that at that point, the difference in velocity due to gravity between your feet and head will become so great that you will be pulled and left looking like spaghetti. As a result, physicists have dubbed what happens “spaghettification.”
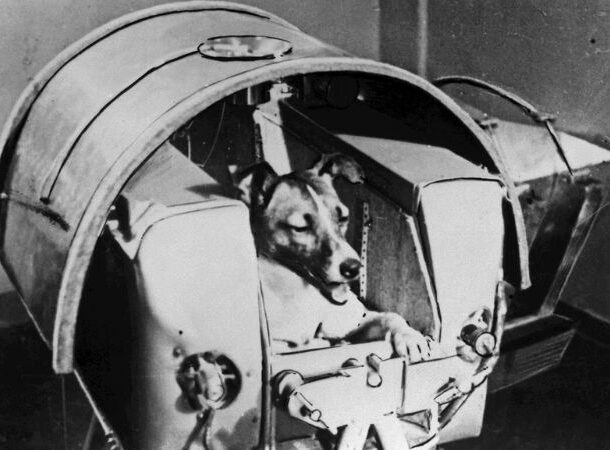
All The Carcasses Orbiting The Earth
 https://science.howstuffworks.com/dead-animals-in-space.htm
https://science.howstuffworks.com/dead-animals-in-space.htm The following item on our list actually makes me feel pretty sick.
Before the concept of manned space flight became a reality, scientists were divided about what it would be like for any living thing to venture out of Earth’s atmosphere. How would space motion sickness, or zero gravity, affect mammals? How would a living body deal with solar radiation?
So, instead of sending humans into such a perilous situation, the US and Russia sent dogs, chimps, monkeys, and other animals into space to examine the effects.
While they are long gone and passed in ways I can not begin to describe, their bodies are still in orbit – and will likely remain there until the end of time.
The Mysterious Perseus Cluster Sound
 https://www.system-sounds.com/black-hole-sound/#:~:text=More videos on YouTube&text=In 2003%2C sound waves were,frequency sound waves ever discovered.
https://www.system-sounds.com/black-hole-sound/#:~:text=More videos on YouTube&text=In 2003%2C sound waves were,frequency sound waves ever discovered. NASA discovered the first enormous sound waves of a supermassive black hole radiating through the Perseus galaxy cluster in 2003. The note’s pitch was the deepest we’ve ever recorded in the universe, a cosmic B-flat 57 octaves below middle C, more than one quadrillion times below the audible.
A lot of scientists wondered if such a sound could be manufactured and used as a weapon and found the answer.
If a 1,100-decibel sound could be produced, the intense waves would be powerful enough to rip space-time apart and create a quantum singularity. In other words, it can potentially make a new black hole. A truly sobering thought.
However, none of this knowledge is actually troubling because it is all impossible. No medium is pressurized enough to produce a 1,100-decibel sound, and no technology comes close to providing the required amount of energy.
The most advanced civilization, however, could create this ultimate weapon by collecting the incredibly dense fluids of an alien atmosphere and using the energy of an entire galaxy. Theoretically.
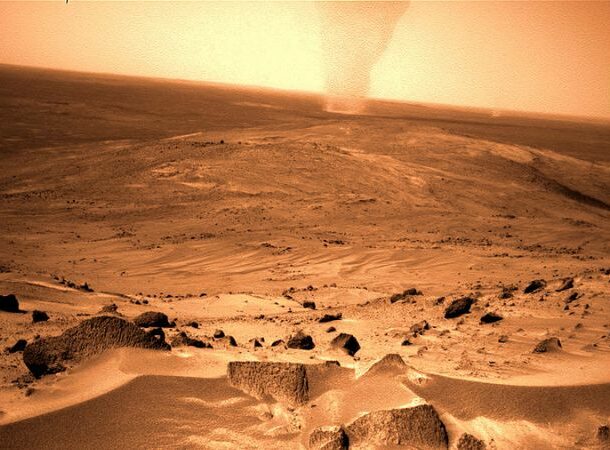
The Mars Dust Devils
 https://www.businessinsider.com/nasa-rover-video-mile-high-dust-devil-mars-2023-10#:~:text=NASA said that Martian dust,of this one on Mars.
https://www.businessinsider.com/nasa-rover-video-mile-high-dust-devil-mars-2023-10#:~:text=NASA said that Martian dust,of this one on Mars. I bet you’re wondering how a dust devil can feature on a list that covers scary space facts. I mean, a dust devil is a tornado’s safer, smaller, and friendlier cousin, is it not?
Well, Martian dust devils are up to ten times taller and 50 times wider than our pitiful terrestrial counterparts, so they constantly threaten our pricey probes and rovers that we invariably send up there.
Apart from all the issues they cause, they’ve also provided a stroke of luck at least once. In 2005, one blew excessive dust and debris off the Spirit rover’s solar panels, improving the rover’s power and allowing it to continue its mission.
If you enjoyed that fact, you’ll want to stick around for the final five items on today’s list. I’ve never heard any of them before!
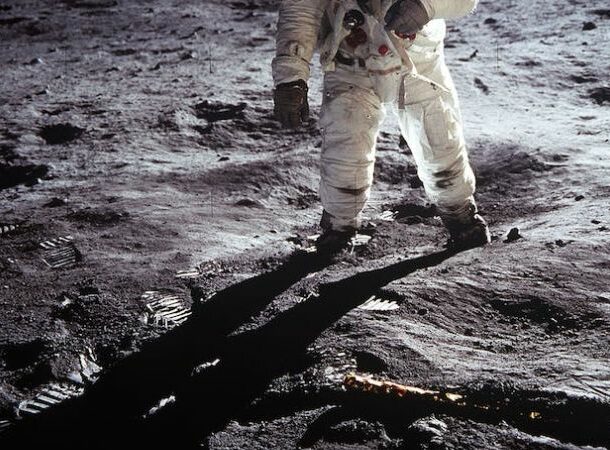
The Moon’s Shadows
 https://www.thestar.com.my/news/true-or-not/2022/11/16/quickcheck-are-shadows-darker-on-the-moon#:~:text=On%20the%20moon%2C%20however%2C%20there,shadows%20are%20not%20completely%20black.
https://www.thestar.com.my/news/true-or-not/2022/11/16/quickcheck-are-shadows-darker-on-the-moon#:~:text=On%20the%20moon%2C%20however%2C%20there,shadows%20are%20not%20completely%20black. When Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong took their first steps on the Moon, they quickly realized something unexpected: the Moon’s shadows were far darker than on Earth. Everything that didn’t get direct sunlight was pitch black. So much so that they couldn’t even see their feet if they stepped into a shadow.
Although they soon discovered they could adapt to the shadows, the persistent contrast between sunny and shaded areas remained challenging.
The Moon’s shadows caused havoc during several Apollo missions. While some astronauts found it impossible to perform maintenance tasks since their own hands obscured what they were doing, others thought they were landing in a cavern because of the deep shadows.
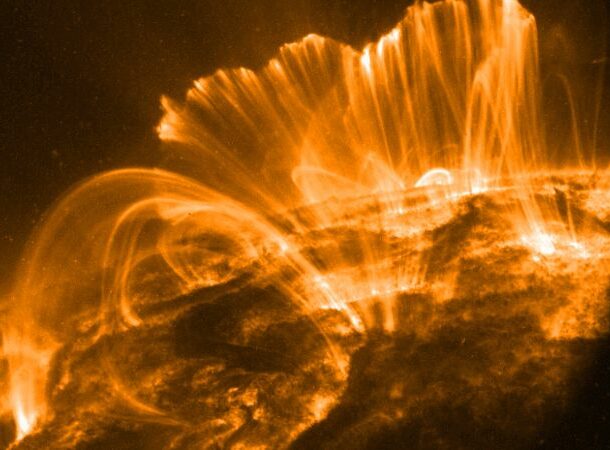
Solar Flares
 https://www.iflscience.com/space/solar-superflare-smash-earth-next-century/
https://www.iflscience.com/space/solar-superflare-smash-earth-next-century/ A solar flare is nothing more than an enormous eruption of radiation from the Sun triggered by the release of magnetic energy.
I know, it doesn’t sound like a big thing – until you realize that we narrowly missed a solar superstorm in 2012, one that could have had enormous repercussions. If it hit us just one week earlier, it would have caused widespread damage 20 times worse than Hurricane Katrina, which would have taken at least 20 years to repair. So why don’t we know about it?
Well, since we missed it, NASA thought it best not to report on it.
Solar flares pose an enormous risk to our way of living. In fact, a 2017 study suggests a “solid chance” of a giant solar flare hitting us within the next century, causing an estimated $10 trillion in damage. The odds of an extinction-level event are one in 1,000 – which should make you sit up straighter. And even though those odds may not sound that scary, the chances of a massive solar flare disrupting our electrical and technological capability are one in eight.
Asteroids
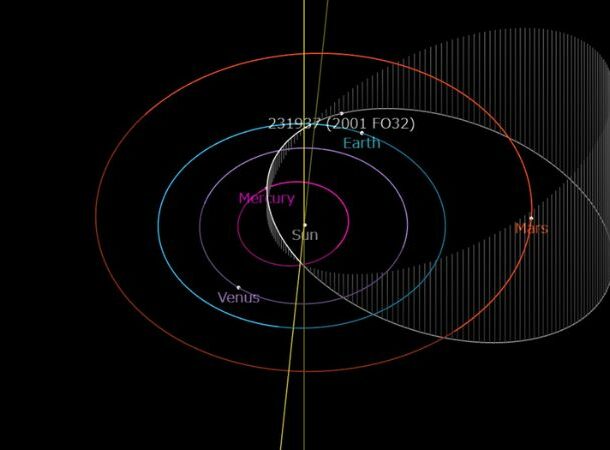 https://www.livescience.com/space/asteroids/a-skyscraper-size-asteroid-flew-closer-to-earth-than-the-moon-and-scientists-didnt-notice-until-2-days-later
https://www.livescience.com/space/asteroids/a-skyscraper-size-asteroid-flew-closer-to-earth-than-the-moon-and-scientists-didnt-notice-until-2-days-later In March 2021, an asteroid passed within 1.25 million miles (2 million km) of Earth, or roughly five times the distance between us and the Moon (called a Lunar Distance, or LD).
Asteroid 2001 FO32, at roughly three times the height of the Eiffel Tower, is bigger than ninety-seven percent of the previously identified asteroids in our solar system. If an asteroid of that size collided with Earth, it would be a global disaster.
If that isn’t enough to scare you, Asteroid 2001 FO32 has been designated by NASA as an Apollo-class asteroid since its trajectory crosses or intersects Earth’s orbit on a comparable plane twice during its own 810-day orbit, increasing the threat of an impact every 2 years. Asteroid 2001 FO32 is classified as a Potentially Hazardous Asteroid (PHA) by NASA, which considers Apollo-class asteroids to be the most dangerous.
And despite all of the info I just gave you, Asteroid 2001 FO32 isn’t the only object to have passed Earth in the last five years. Or even the closest. Several came closer to Earth than the Moon, and at least three big ones were only discovered after they had passed us.
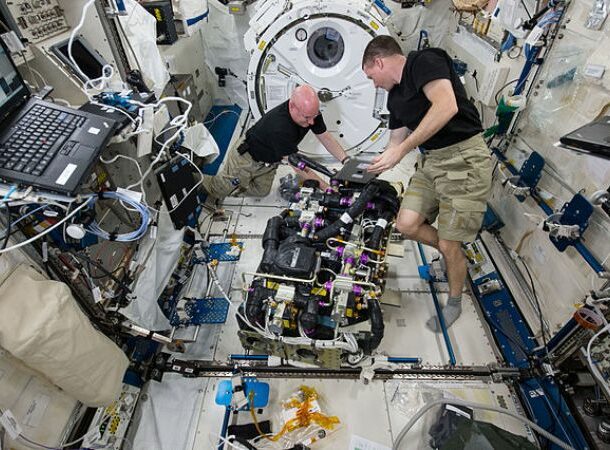
Carbon Dioxide Poisoning On The ISS
 https://www.airspacemag.com/daily-planet/why-living-space-can-be-pain-head-180951507/
https://www.airspacemag.com/daily-planet/why-living-space-can-be-pain-head-180951507/ The International Space Station (ISS) has a higher-than-average carbon dioxide concentration that comes with a massive amount of unfavorable side effects. Sleeping difficulties, headaches, and irritation are very common – in fact, nearly all astronauts endure headaches at the start of their missions.
Unlike on Earth, where carbon dioxide leaving the body disperses into the air, CO2 exhaled by astronauts forms a cloud above their heads. Even though fans disperse the CO2 throughout the station, the levels cannot be brought down to acceptable levels. Chronic exposure to high CO2 levels can lead to memory problems, hearing disorders, nausea, sleep disorders, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting.
So it might be a good idea to hold off on traveling to Mars until we at least get that bit sorted out.
Solar Eclipses
 https://www.pasco.com/eclipse
https://www.pasco.com/eclipse The conditions in the path of totality may shift quickly during a total solar eclipse. Temperatures drop, and the immediate area goes dark, often leading to changes in wind direction.
What many of us don’t realize while we stare in awe at the sun is that animals often become very confused during solar eclipses. Not only larger animals and mammals but all living things, even microbes. We are yet to do proper testing on the effects of eclipses on plants and animal life in space.
Another interesting fact is that eclipses disrupt certain radio wave frequencies – and we’re still trying to figure out why. Scientists suspect it has to do with how the sun interacts with the planet’s ionosphere, which has been shown to change in the wake of solar flares and storms. There’s still a lot we have to figure out.
Communication Delays
 https://www.nasa.gov/missions/tech-demonstration/space-communications-7-things-you-need-to-know/#:~:text=When the planets are at,minutes to receive a response.
https://www.nasa.gov/missions/tech-demonstration/space-communications-7-things-you-need-to-know/#:~:text=When the planets are at,minutes to receive a response. Phone calls on Earth are almost instantaneous. When we travel deeper into space, it turns into a different ball game.
A long-distance call from the US can travel about 18,000 mi, but if we’re thinking about space communication, those signals have to travel millions of miles.
For example, a one-way radio signal to Mars will take anywhere from 4.3 to 21 minutes, so getting a message out and receiving a reply can take up to 42 minutes.
It is also possible for the Sun to interfere with communication between Earth and Mars to the point that astronauts become cut off from Earth for weeks at a time. In addition to preventing astronauts from interacting socially, they will also prevent them from getting live support when they encounter technical difficulties.
Space Adaptation Syndrome
 https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/05/080521112119.htm
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/05/080521112119.htm Can you imagine what it would feel like if your brain couldn’t figure out where up and down was?
Space sickness, also known as space adaptation syndrome, happens when an astronaut’s body struggles to adapt without the Earth’s gravitational pull. It’s been said to be a lot like motion sickness, but it comes with an added dash of disorientation, intense headaches, serious discomfort, and occasionally – nausea and vertigo. And trust me, throwing up in space is SO much worse than you can imagine.
It’s not the lack of gravity that makes people sick, but rather the abrupt change in gravitational force.
Space Pandemics
 https://www.nature.com/articles/nrmicro1264
https://www.nature.com/articles/nrmicro1264 Have you ever wondered why technicians and scientists working on the ISS dress like hospital surgeons? For the same reason, we do it down here – to avoid the transmission of germs.
Some pathogens are known to be capable of surviving in space, and we would not want to bring them back to Earth, nor would we want to send any of our super-resistant bugs there.
For example, Deinococcus radiodurans ranks as one of the most robust organisms known to science. It is a bacteria, not a virus, and can withstand a gamma radiation dose of 5,000 grays, whereas 5 grays is enough to kill an adult human. The only easy way to kill it is to boil it for 25 minutes. (Something like botulinum dies in 2 to 7 minutes – to put it into perspective).
Deinococcus has been found in various environments, from spoiled food to sewage and household dust. Can you imagine what would happen if we were to leave it in an alien environment during a space mission?
Psychological Consequences
 https://www.theverge.com/2013/5/30/4377120/nasa-mars-psychology-wearable-sensors-astronauts
https://www.theverge.com/2013/5/30/4377120/nasa-mars-psychology-wearable-sensors-astronauts Currently, astronauts have been proven to benefit psychologically when they see the Earth in orbit while on the ISS. We have yet to learn what will happen if they start venturing further away from home.
Homesickness, depression, and even full-blown psychosis are some of the predicted consequences of not being able to see our home planet. The concerns are of such a nature that scientists have already given the obstacle a name – “Earth-out-of-view phenomenon.”
There are also legitimate concerns that crewmates will turn violent on one another, as the biosphere tests we’ve conducted have already ended in crewmembers refusing to speak to one another except when dealing with critical tasks. Scientists are working on intensive mental health evaluation and therapy protocols for long space voyages due to the likely risks of a violent disagreement during the trip.
Deaths In Space
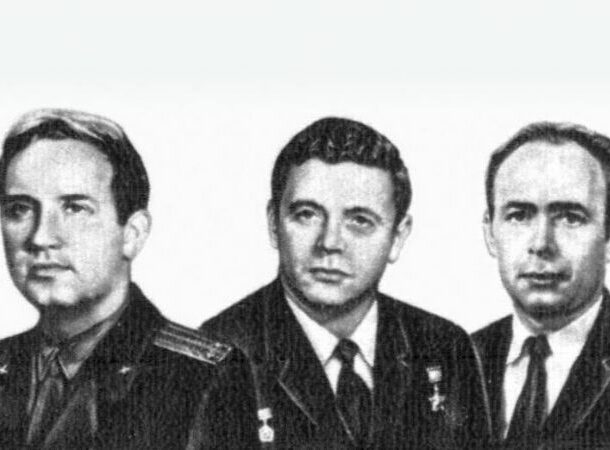 http://uk.businessinsider.com/what-if-someone-dies-in-space-2015-4?r=US&IR=T
http://uk.businessinsider.com/what-if-someone-dies-in-space-2015-4?r=US&IR=T To date, only three people have died in space. Their names were Viktor Patsayev, Vladislav Volkov, and Georgi Dobrovolski.
Should someone pass during an extended space mission, one possibility is to launch the body into space. However, the United Nations prohibits dumping litter, including bodies, in space due to concerns that they will collide with spacecraft or contaminate other planets.
Another option is to keep the body aboard the spaceship and bury it when they return to Earth. However, this would endanger the lives of other astronauts.
If we ever make it to Mars, the body could be used as fertilizer – but we’re not even sure if that would be effective in Mars’ atmosphere.
NASA is collaborating with Promessa, a burial company, to develop the “Body Back.” Body Back seals a corpse in a sealed container and attaches it to the spaceship’s exterior. As the spacecraft travels through space, the body freezes, shakes, and ultimately breaks into small, fine particles that can be brought home.
Gamma-ray Bursts
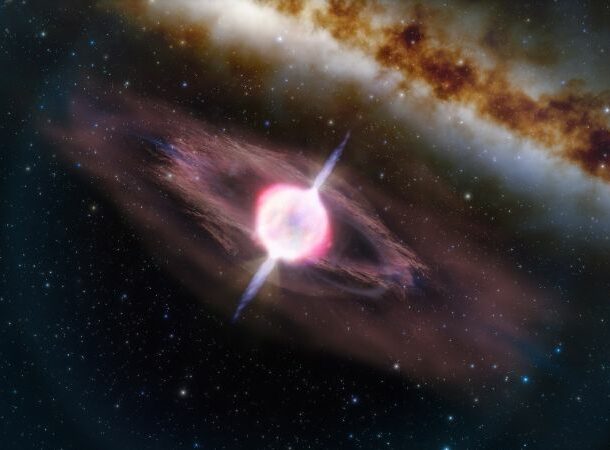 https://www.livescience.com/49040-gamma-ray-burst-mass-extinction.html
https://www.livescience.com/49040-gamma-ray-burst-mass-extinction.html Gamma-ray bursts, or GRBs, are high-frequency electromagnetic bursts that produce more energy in a single second than our Sun could hope to produce in ten billion years. Scientists believe these volatile bursts are caused by neutron star collisions or exploding stars.
If a GRB ever strikes our planet, it would be devastating. We would very well face mass extinction. It would deplete our ozone layer and cause a chain reaction that would chemically devastate our atmosphere. On top of that, the high amounts of radiation these bursts contain would cause radiation sickness in those who survive the initial impact of the burst due to the damage it caused to our ozone layer.
While gamma-ray bursts mostly occur in distant dwarf galaxies, they have also occurred much too close to home for comfort, and scientists theorize that they may have caused previous mass extinction events on Earth.
Solar Tornadoes
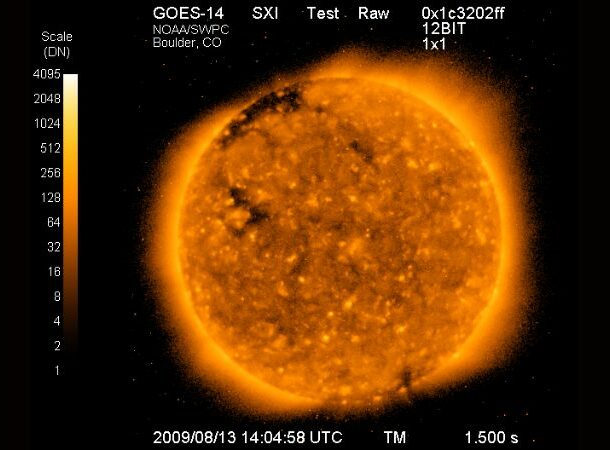 https://www.space.com/plasma-tornado-sun-north-pole-video
https://www.space.com/plasma-tornado-sun-north-pole-video The SDO, or the Solar Dynamics Observatory, has been recording incredible high-definition color clips and images of our sun for years. It recently recorded the solar system’s “tallest tornado” spinning top the sun’s North Pole in March of 2023. This swirling mass of boiling plasma grew in the Sun’s atmosphere for three days, reaching an astounding height of roughly 111,000 miles before it collapsed into a plume of magnetized gas.
Solar tornadoes form on magnetic lines with points fixed to the sun’s surface and can form on each pole. These sun twisters are caused by superheated gas that bursts from the Sun and spirals along its magnetic field, creating these tornado-like storms.
These planetary-sized magnetic fields twirl up the plasma to form the signature corkscrew shapes of a Kansas tornado- except, it ain’t Kansas, Toto.
The Overview Effect
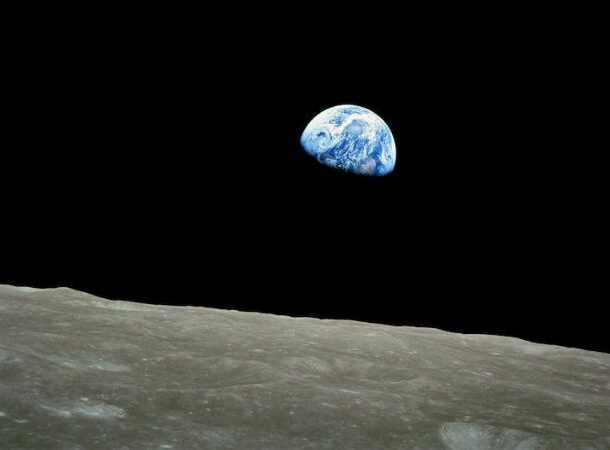 https://www.skyatnightmagazine.com/space-missions/overview-effect
https://www.skyatnightmagazine.com/space-missions/overview-effect Ok, our last item might not be scary per se, but I think it becomes scary once you realize there might be something missing in all of us.
The overview effect has to be one of the most uncommon psychological repercussions ever identified, observed, and studied – only 534 people have gone through the conditions that triggered it. When space travelers in orbit or on the moon first see our planet as a whole, many report feeling a profound sense of proportion and perspective, and this has come to be known as the overview effect.
The effect, coined by writer Frank White, can be incredibly moving, disorienting, inspiring, and psychologically challenging, as seeing the entire Earth profoundly shifts a person’s perspective. Astronauts have returned home with a renewed sense of humanity’s interconnectedness, the meaninglessness of cultural boundaries, and a passion for protecting the Earth’s environment.
All in all, this is something I wish we could all experience – before we destroy everything we love to take for granted.



























