We frequently encounter the universe as an intriguing subject. Space travel, with its potential for colonizing other planets and discovering intelligent lifeforms elsewhere in the universe, piques our curiosity. For ages, gazing at the cosmos has fueled our imagination and even influenced our journeys and existence. Although our forebears were often proficient astronomers and mathematicians, their abilities and resources only enabled them to explore the universe to a certain extent. For this compilation, we have combed through recent space news to present you with some of the most cutting-edge discoveries made by scientists in the field.
From a cosmic collision which produced tons of gold to a star which is basically a massive diamond, the space discoveries we have made in the past decade have pushed our understanding to new heights. They also have often invalidated past theories, forcing astronomers to consider alternatives for how we came to exist in the grand universe. From the coldest place in the universe to a comet which produces its own alcohol, put on your space suit as we blast into these 25 Recent Space Discoveries That Blew Our Minds.

Earth-like planets
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia In 2013, astronomers confirmed the presence of 20 billion exoplanets in our Milky Way Galaxy alone which are similar to Earth (and thus may contain life). With the billions of galaxies in the universe, that’s billions of billions of planets which may harbor life.
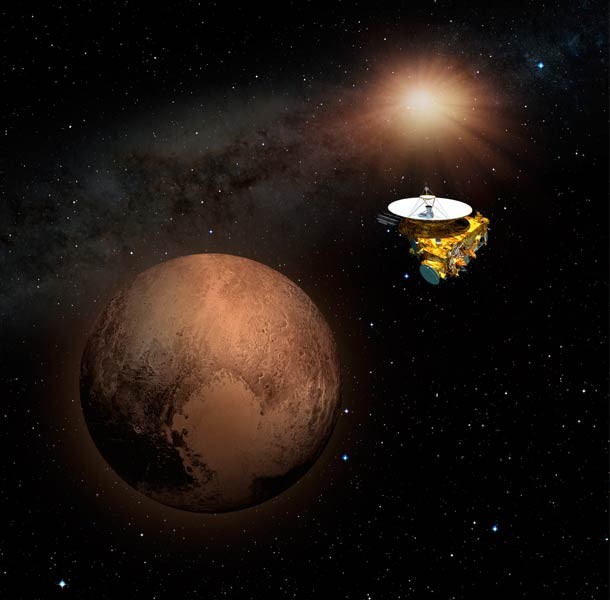
Pluto's not lost yet
 Source: Space, Image: Shutterstock
Source: Space, Image: Shutterstock Space lovers were devastated in 2006 when Pluto was demoted from a planet to a dwarf planet. Those refusing to accept its fate were rewarded in 2015 when the New Horizons spacecraft passed by the hunk of ice and rock, revealing that it acts more like a true planet than a dwarf planet. The probe found Pluto has a gravity strong enough to hold onto its atmosphere and deflect charged particles from solar wind.
The gold star collision
 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA The year 2013 was a fantastic year for astronomy. Astronomers also detected the collision of two stars which produced tons and tons of gold, weighing many times the mass of our own Moon.
Martian tsunamis
 Source: Space, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Space, Image: Wikipedia Scientists have recently released evidence that massive tsunamis may have rocked the Martian landscape. A discovery that blew the minds of many in the space community, the researchers posit that two meteor strikes caused huge tidal waves which would have produced 165 feet (50 m) high waves.
The Godzilla of Earth
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikimedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikimedia Our planet is one of the larger-sized rocky planets, but in 2014 scientists found a planet twice its size and 17 times as heavy. Though planets of this size were thought to be gas giants, this planet – named Kepler-10c – is remarkably similar to our own and has been called the “Godzilla of Earth”.
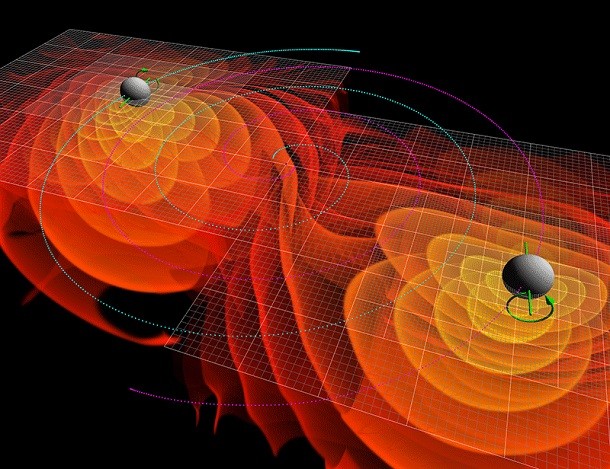
Gravitational waves
 Source: ABC Science, Image: Wikipedia
Source: ABC Science, Image: Wikipedia Albert Einstein declared his finding of gravitational waves back in 1916, nearly a century before scientists confirmed their existence. The science world was thrilled by their discovery in 2015, revealing that space-time could ripple just as still water on a pond ripples when a stone is tossed into it.
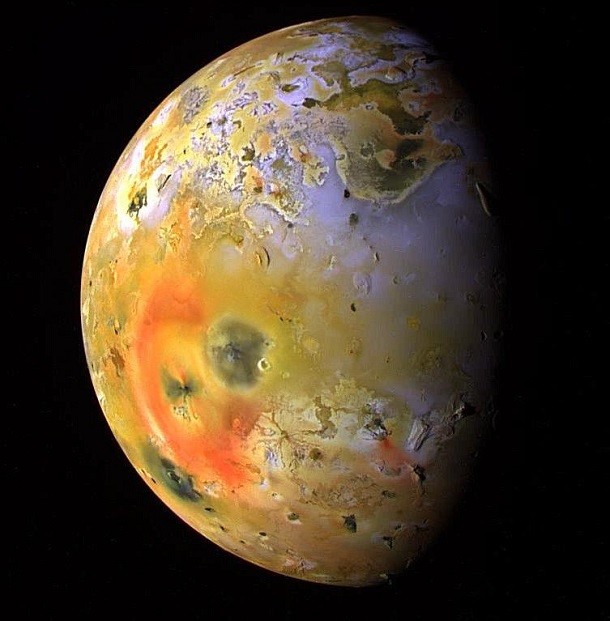
A volcanic moon forms mountains
 Source: Discovery News, Image: NASA
Source: Discovery News, Image: NASA New research has revealed how mountains on Jupiter’s volcanic moon Io form. Though mountains on Earth grow in long chains, Io’s mountains are mostly solitary. The moon is so volcanically active that a five inch layer of molten lava covers its surface every 10 years. By looking at this rapid rate of eruption, scientists have concluded that massive pressure on Io’s core causes fractures which head to the surface to release pressure.
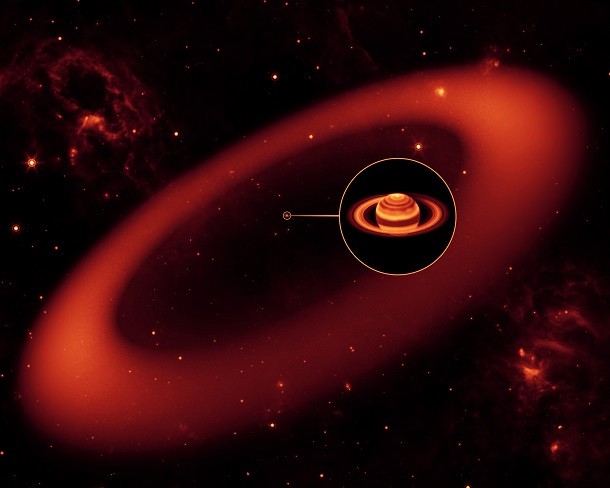
Saturn's massive new ring
 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA Astronomers have recently discovered a massive new ring around Saturn. Situated 6-18 million miles (3.7-11.1 million kms) from the planet’s surface, the new ring spins in the opposite direction of the other rings. The new ring is so thinly scattered that you couldn’t tell if you stood inside it, despite the fact that a billion Earths could fit within it. Since the ring is quite cool, about -316° F, it was only recently discovered when using an infrared telescope.
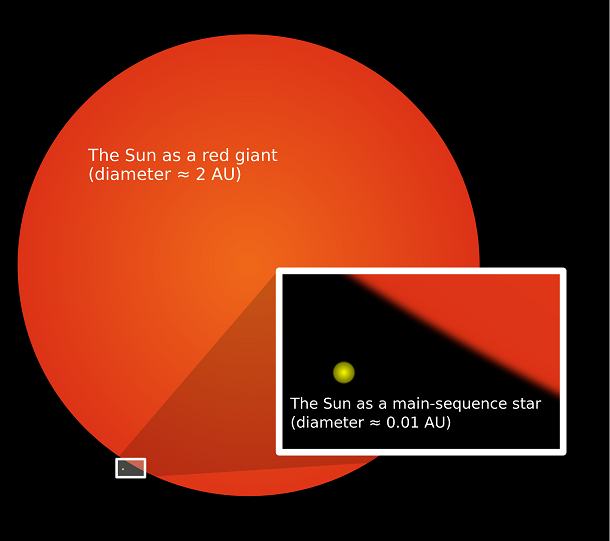
Dying stars produce new life
 Source: Science X Network, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Science X Network, Image: Wikipedia Once a star burns up all the hydrogen in its core, it expands to many times its normal size. As it expands, it engulfs and consumes nearby planets. Scientists have recently found, though, that more distant planets could warm up and become hotbeds for terrestrial life. In our solar system’s case, the Sun will extend past Mars’ orbit, warming conditions on the moons of Jupiter and Saturn enough to develop life.
Oldest star in the universe
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia A few hundred million years is junk change in the lifespan of the universe (which is 14 billion years old). The oldest star ever discovered – SMSS J031300.36-670839.3 – is bafflingly nearly as ancient at 13.6 billion years old.
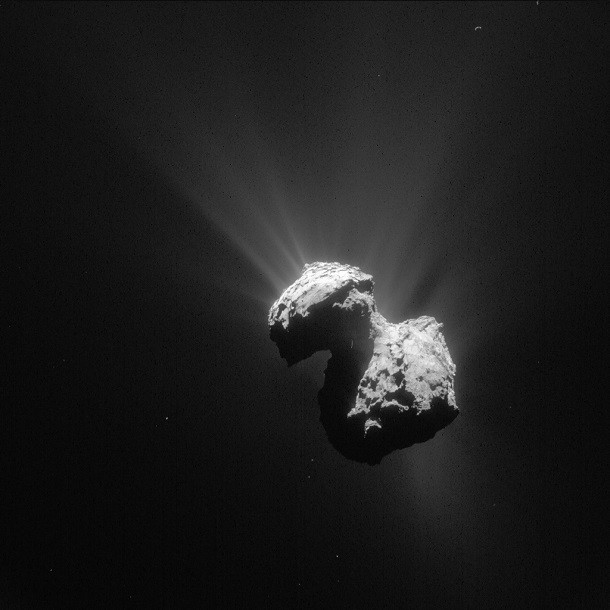
True oxygen in space
 Source: ESA, Image: NASA
Source: ESA, Image: NASA Oxygen is naturally a highly reactive gas, leading it to bond with other substances to exist in space. The discovery of molecular oxygen – the same kind we breath – in the atmosphere of infamous comet 67P deepens our understanding of cosmic gases and gives hope that oxygen can exist in a form we humans can use in other places in the universe.
It looks like you enjoy space related lists, why not check out these 25 space images that will blow your mind?
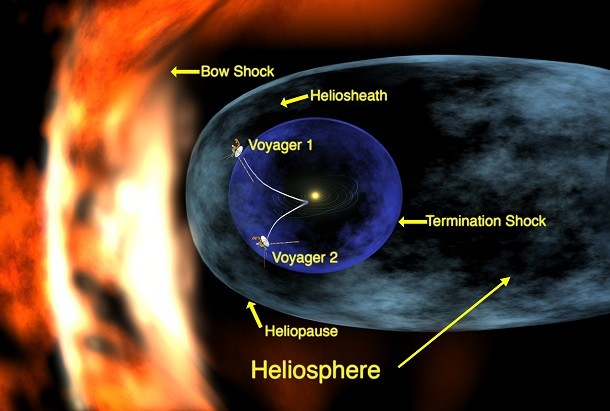
Cosmic Purgatory
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia Astronomers have defined a new region of space discovered by the Voyager 1 probe as cosmic purgatory. Just beyond the reach of the Solar System, this area has a magnetic field twice as strong to create a barrier to interstellar space. Charged particles emitted from the Sun were also noted to slow down and even turn around.
Flags on the moon
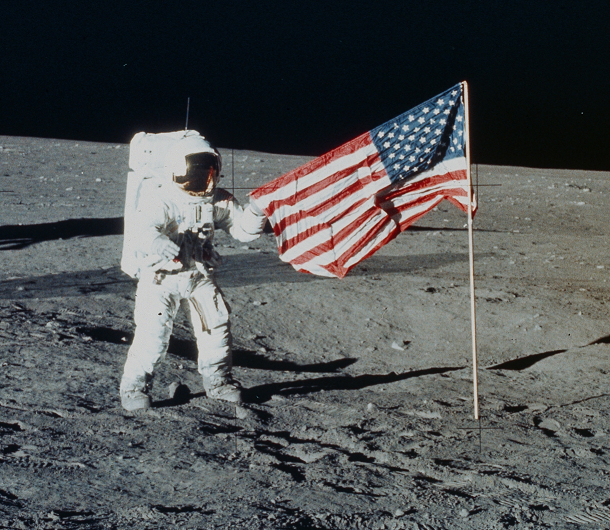 Source: Discovery News, Image: NASA
Source: Discovery News, Image: NASA All the Apollo missions which visited the moon left an American flag in our most famous satellite’s soil. Though mostly ceremonial as, by treaty, no one can own the moon, the flags were expected to have been reduced to bleached-white scraps of nylon after years of cosmic radiation and bombardment. When the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter pointed its telescopes at the landing sites in 2012, it found the flags were (still) shadows of their former selves, meaning the fabric was likely still intact.
The hyperactive galaxy
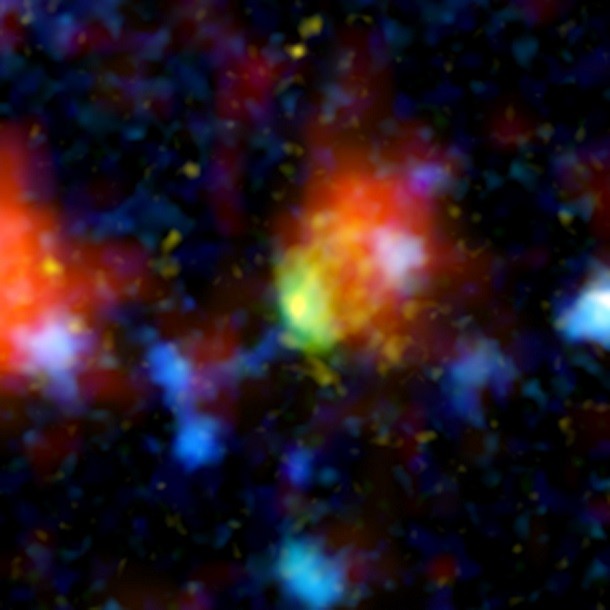 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA A starburst galaxy located 12.2 billion light years from Earth, the Baby Boom Galaxy was discovered in 2008. The aptly named galaxy takes the cake as the brightest starburst galaxy in the very distant universe, thanks to its incredibly rapid star formation. While our Milky Way gives birth to a new star, on average, every 36 days, a new star is born every 2 hours in the Baby Boom.
The coldest spot in the universe
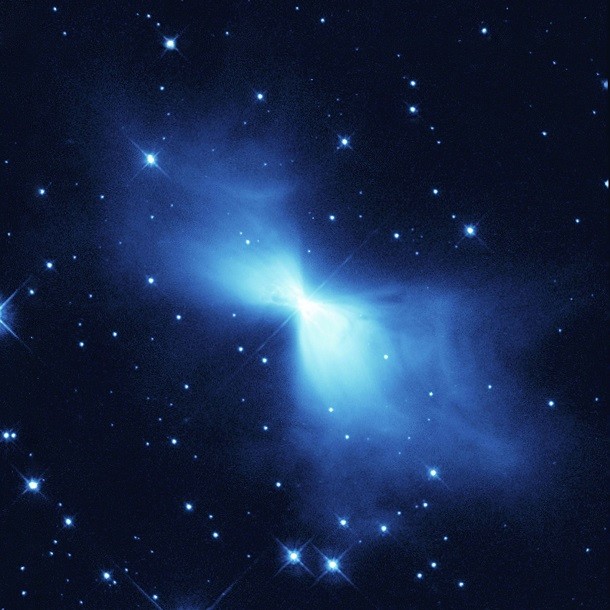 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA The coldest place in the universe is the Boomerang Nebula, registering almost no heat at all. Touching the bottom rungs of the thermodynamic scale at just about absolute zero, the nebula glows blue and shines brightly due to light reflecting off its dust.
The shrinking icon
 Source: Discovery News, Image: NASA
Source: Discovery News, Image: NASA Jupiter’s iconic Great Red Spot has been shrinking over the past century, now only half its original width. Since what we can see of the planet is basically a mass of swirling cloud streams, it’s not surprising that the hurricane of a spot can change size. Even more bizarre, though, is a line of waves just near the equator. Though we’re not sure what causes them, they look remarkably similar to waves which form in Earth’s atmosphere just before a cyclone.
Smallest planet
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia The smallest planet we’ve yet discovered was found in 2013. Named Kepler-37b, the planet is slightly larger than our Moon, but – at three times closer to its star than Mercury is to the Sun – scorches everything on its surface with a tepid 800°F (425°C).
Stars dying prematurely
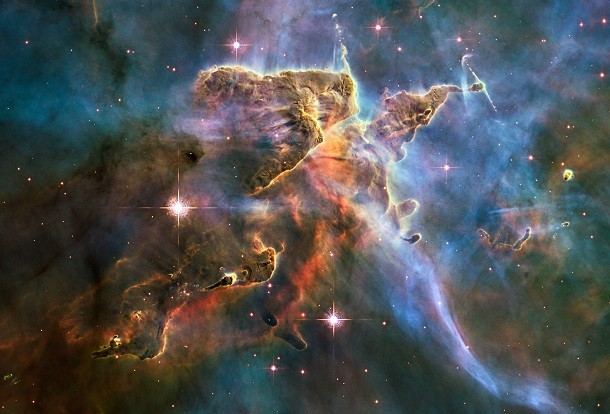 Source: Science X Network, Image: Wikimedia
Source: Science X Network, Image: Wikimedia Some stars in the robust star-forming region known as the Carina Nebula were found in 2016 to be prematurely dying. About half of the stars skip their Red Giant stage, cutting out millions of years in the traditional star life cycle. While we’re unsure what causes this effect, premature death has only been seen in sodium-rich or oxygen-poor stars.
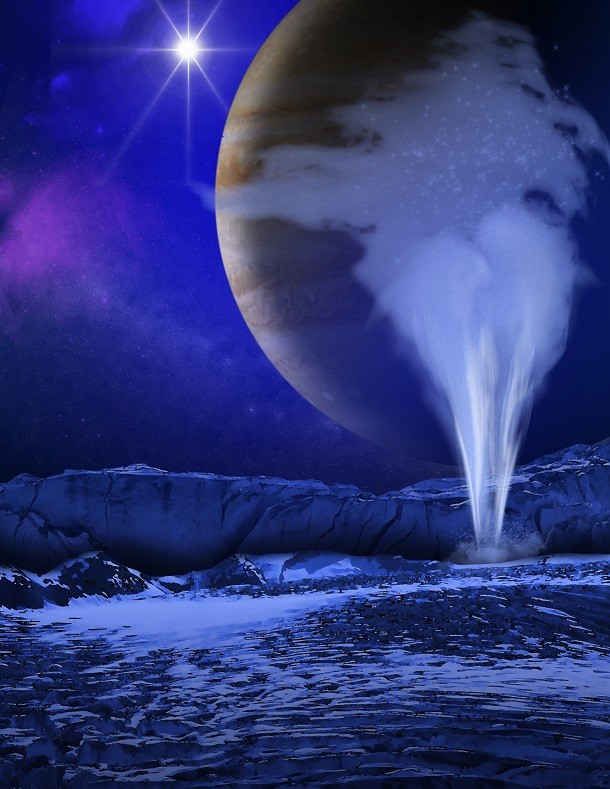
Where we should be looking for life
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikimedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikimedia We may not need to look to other planets for future human bases but rather to moons. When it passes near to Jupiter, the icy moon Europa shoots out 15,000 pounds (6,800 kg) of water per second from its cracked southern pole. Scientists have recently worked out that a probe would relatively easily be able to analyze the water’s contents before they fall back to the planet’s surface. Such studies could help us determine if life exists or is possible on Europa.
The massive diamond star
 Source: Chicago Tribune, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Chicago Tribune, Image: Wikipedia Often referred to by its nickname “Lucy”, star BPM 37093 is a white dwarf star located about 20 light years from Earth. The star is remarkable – basically a massive diamond the size of our moon. If assessed by jewelers, the diamond would be 10 decillion carats.
The real ninth planet
 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA Though Pluto was demoted, scientists believe there may be a massive planet orbiting the Sun beyond Pluto. Using mathematical laws, scientists have worked out that a planet as big as Neptune must be in orbit, though we’re still looking to catch a glimpse of this elusive planet.
A noisy vacuum
 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA In September 2013, NASA released audio recordings of plasma waves, the first sounds ever recorded in interstellar space.
The brightest supernova
 Source: Science X Network, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Science X Network, Image: Wikipedia Detected in 2015, ASASSN-15lh is the brightest supernova ever seen, measuring over 570 billion times the luminosity of our Sun. Even stranger, scientists found the supernova brightened a second time about two months after its peak brightness.
An asteroid with rings
 Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia
Source: NASA, Image: Wikipedia Though it’s common for massive gas giants to have orbiting ring systems, rings are quite rare among other celestial bodies. Scientists were fascinated upon discovering rings around the Georgia-sized asteroid Chariklo. The asteroid has two rings likely made of ice water which came from a previous collision.
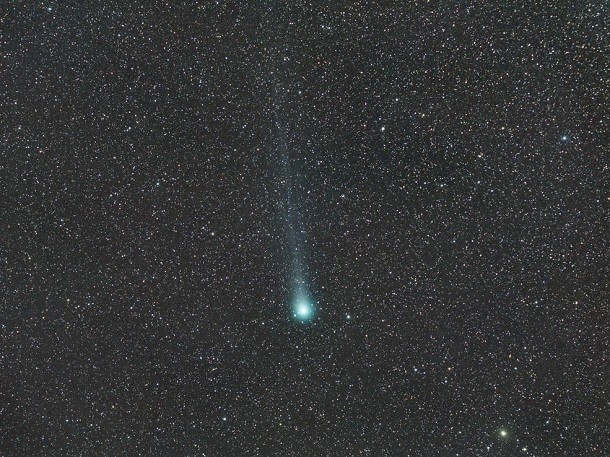
The alcoholic comet
 Source: NASA, Image: NASA
Source: NASA, Image: NASA Comet Lovejoy captured astronomers’ (and alcoholics’) imagination in 2015. While studying the fast-flying hunk of ice, scientists discovered the comet ejected the same type of alcohol we drink – at a rate of 500 wine bottles per second. It also ejects a simple sugar, glycolaldehyde, making us wonder if this comet is its own one-stop fermentation brewery.



























