Are you acquainted with the gods of ancient Egypt? The ancient Egyptians were among the most spiritual societies on Earth, holding strong beliefs in the supernatural. From this belief system emerged numerous gods of ancient Egypt. If there was a potential situation or place that could have its own god, there’s a good chance one existed. Though most deities were recognized on a local level, some such as Ra, Osiris, and Thoth achieved national prominence. In the following list, we compiled (not physically, that’s for the archaeologists and tomb raiders) intriguing details about these ancient Egyptian deities. Are you prepared to dive into this captivating knowledge about these deities? Here are 25 facts about ancient Egyptian gods that might surprise you.

Cover Image CC via Insights Unspoken via Flickr
Like many young religious traditions, religion in pre-dynastic Egypt was mostly animistic, making various animals, plants, or things the homes of spirits.
 Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Wikipedia Many of today's well-known Egyptian gods harken back to the animistic times. Take Anubis, the god of funerals and death. He is depicted with the head of a jackal since the animals often were seen at the desert's edge where Egyptians buried their dead.
 Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Wikipedia Good news for Gator fans: the Ancient Egyptians had a gator god! (Well, technically he had a Nile crocodile head.) Sobek was one of the most powerful and longest lasting gods. As guardian of waterways, Sobek enjoyed eating flesh, like most crocodiles. To show reverence, many Ancient Egyptian temples kept live crocs in pools.
 Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia
Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia Though the Ancient Egyptians had over 2,000 gods, most were only known locally in small parts of the empire.
 Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia
Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia Just like we have multiple branches of Christianity today - Catholicism, Methodism, Eastern Orthodox, etc. - Ancient Egyptians also had multiple schools of religious thought, each claiming it was superior to the others.
 Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Nancy Ross via YouTube
Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Nancy Ross via YouTube The sun god Ra has one of the most interesting stories among all the Ancient Egyptian gods. Every night, it is said this god was eaten by Nut, the sky goddess, only to be reborn the following sunrise.
 Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia
Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia The worship of Egyptian gods was one of the most durable religions in the world, lasting over 3,000 years. In contrast, Buddhism has been around for only 2,500; Christianity for 2,000; and Mormonism for 200 years.
 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia Whenever a new pharaoh took power, he would often promote the local god from his school of thought to be the primary national god. For example, when power shifted to Thebes during the Middle Kingdom years (2000 BC to 1700 BC), Amun became the national god after fusing with Ra to become Amun-Ra.
 Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Ancient Egypt Online, Image: Wikipedia Beyond originating from Ancient Egyptians' animistic beliefs, the incorporation of animal features in gods had another important use: showing the deity's mood. If a god was enraged, its head may have been depicted as a fearsome lion; if calm and gentle, it may have had a cat's head instead.
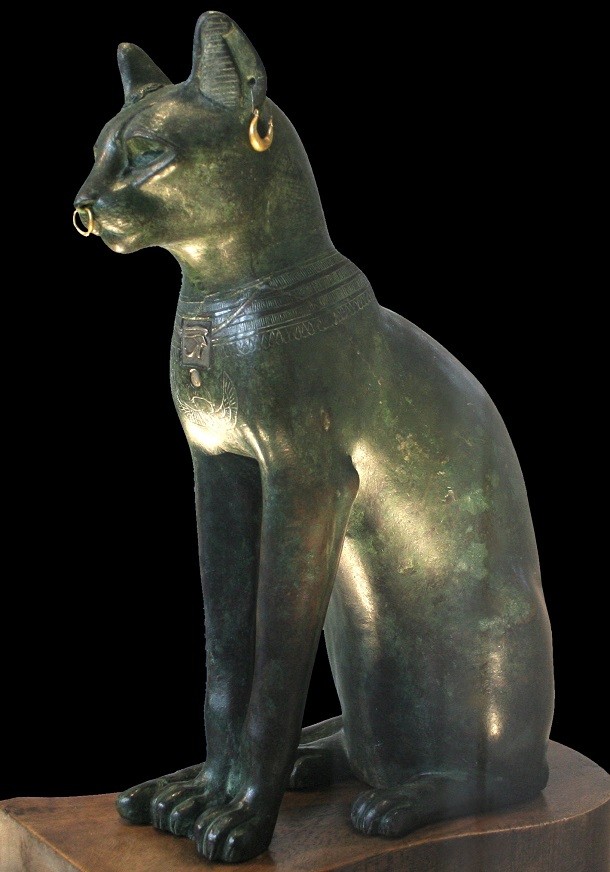 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia Egyptian gods were most often portrayed with a human body and an animal head. Images of an animal body and human head were often used to represent kings.
 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia Egyptian gods were often seen holding the mysterious Ankh symbol. Symbolizing eternal life, the cross with a handle was known as the key of life and reinforced the permanence and eternity of their rules.
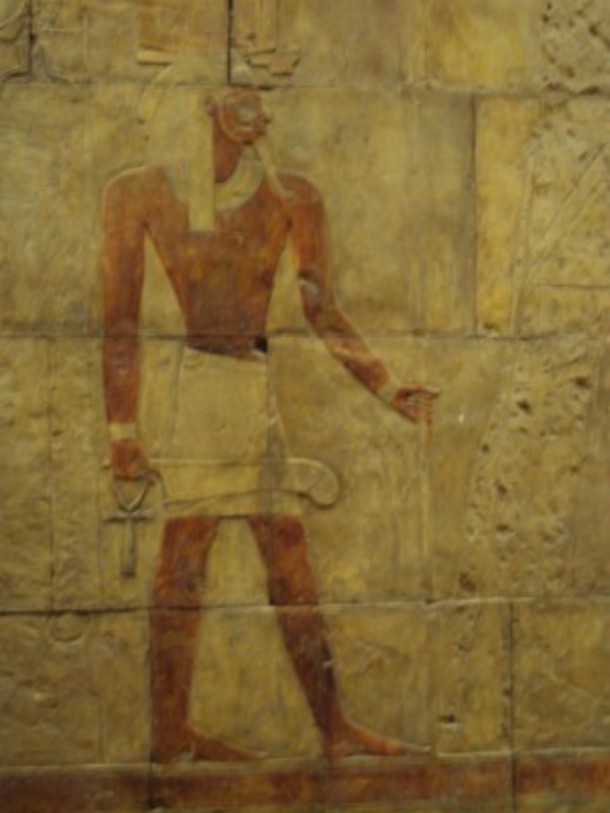 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia
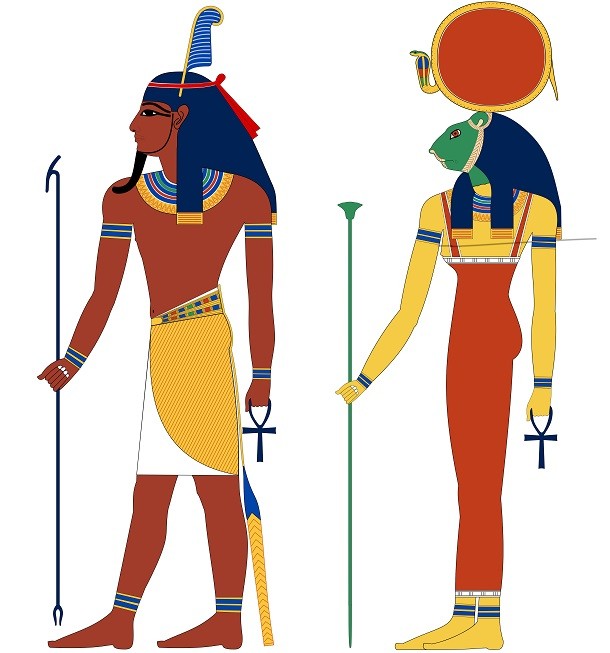
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia Though it may seem difficult to determine if a god is male or female in many of the ancient paintings, here's a trick: male gods had dark reddish-brown skin, while goddesses had yellow skin to signify their indoor lifestyles.
 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia
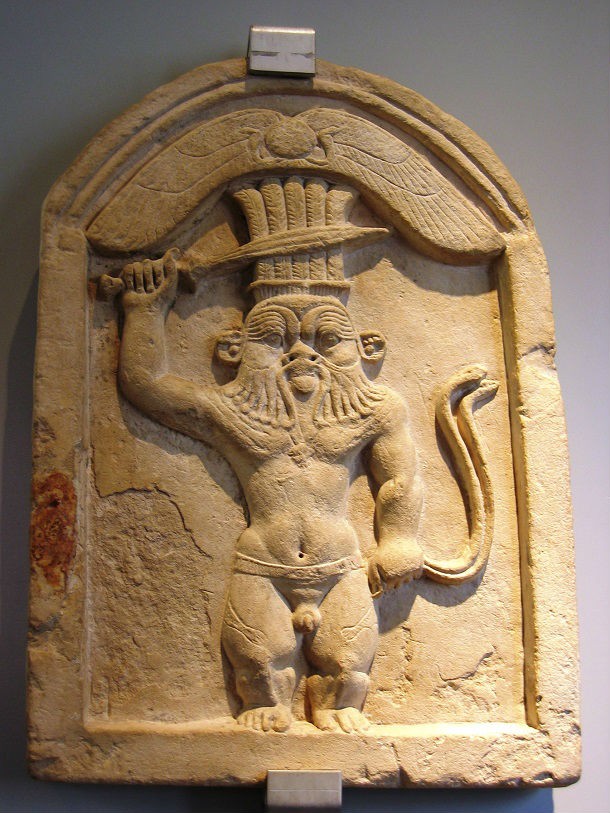
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia The god Bes was one of the busiest gods in Ancient Egypt, acting as the god of babies and mothers, households, nightmares, and even scorpion bites.
 Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikimedia
Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikimedia Ancient Egypt was polytheistic for most of its existence, barring a short period during the Eighteenth Dynasty when Pharaoh Akhenaten forced the country to become monotheistic. This one-god devotion was centered around Aten: the disk of the sun, attributed to Ra.
 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikipedia Beyond the gods, demons played a strong role in Ancient Egyptians' belief systems. Though more powerful than humans, they were less powerful than gods but were generally immortal and could be in multiple places at once.
 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia One of the best-known symbols of Ancient Egypt, the scarab beetle represented resurrection and protection. Locals often wore scarab amulets for safety, a reference to the scarab-headed god of rebirth: Khepri.
 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia The Ancient Greeks drew many parallels between their gods and the Ancient Egyptians'. While Alexander the Great was moving through the region, he stopped in to consult the Oracle of Amun: the god Greeks felt represented Zeus. Alexander was so well-known throughout Ancient Egypt that the Oracle of the Siwa Oasis even called him the son of Amun.
 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
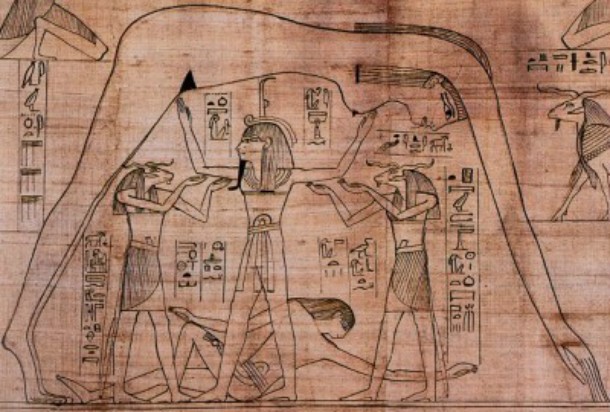
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia A mismatch made in heaven: Shu (center), the god of dry air and sunlight, was married to Tefnut, the god of moisture who controlled the rain.
 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
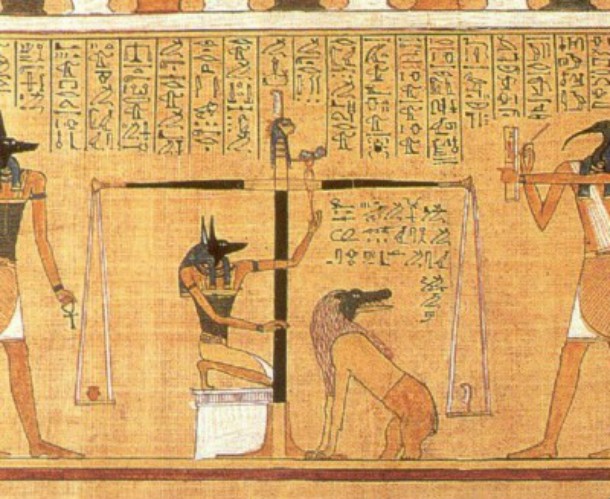
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia The pharaoh was the intermediary between the gods and Ancient Egyptians. His role was to carefully preserve the delicate balance by keeping good relations with the gods. Locals believed that, upon his death, a pharaoh would become a god if his heart weighed less than a feather.
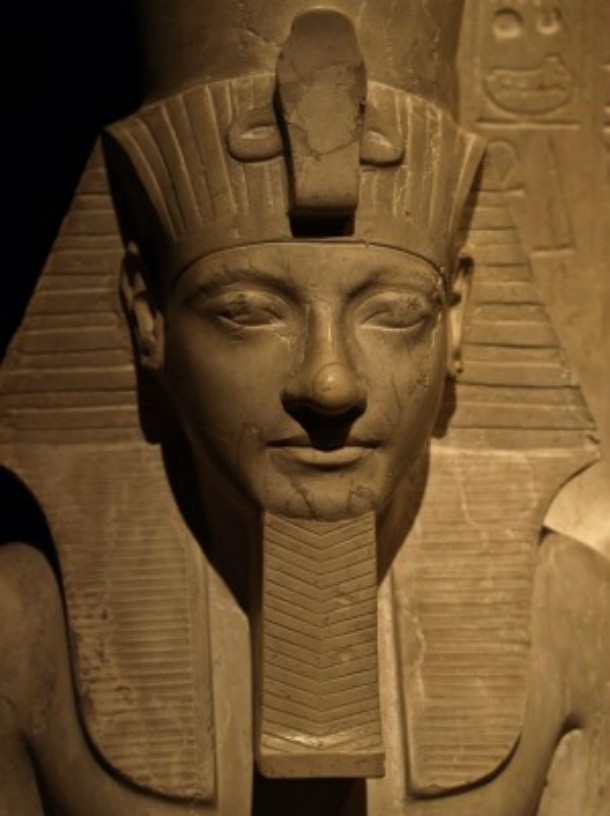 Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia
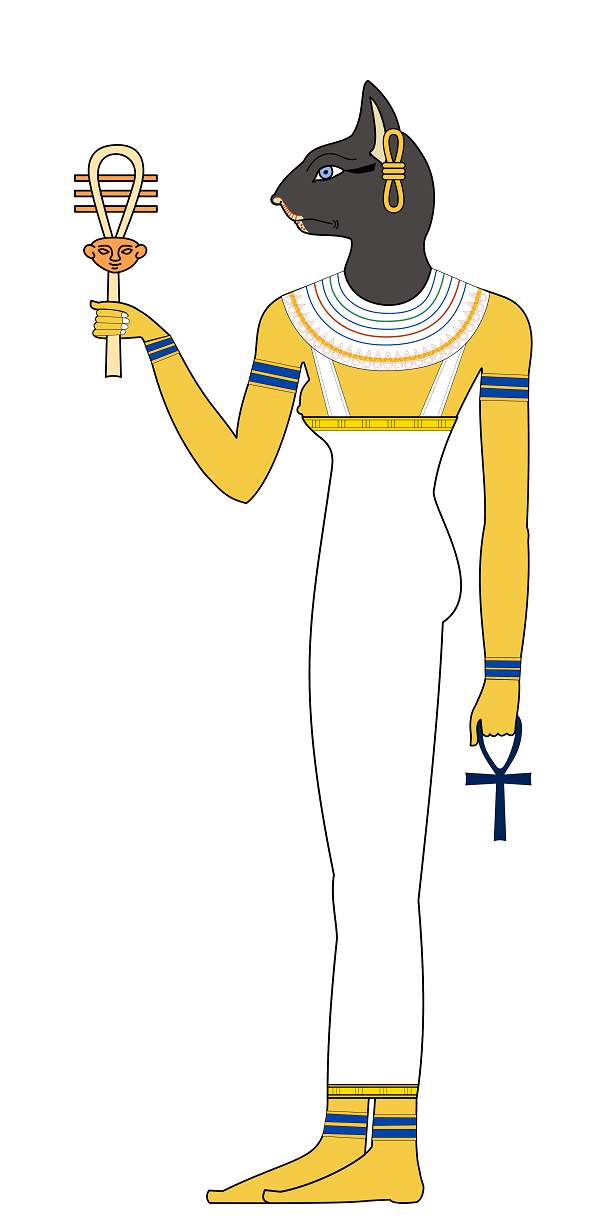
Source: National Geographic, Image: Wikipedia The goddess Bastet had a woman's body and a cat's head. Followers of her cult revered cats so much they mummified the felines when they died. Nearby her primary temple in the town of Bubastis, archaeologists have even discovered an enormous mummified cat cemetery.
 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia Religious life in Ancient Egypt was largely elitist. Only priests, priestesses, and the Pharaoh and some members of his family were allowed inside temples. Normal Egyptians had to stop at the temples' gates.
 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia Despite his importance, the god Geb (bottom middle) never achieved a cult following like others such as Osiris and Amun. As the god of the Earth, it was believed his laughter caused earthquakes.
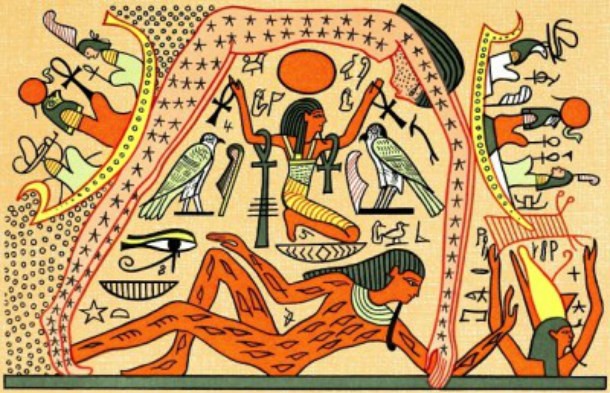 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikimedia
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikimedia The Ancient Egyptians erected countless statues of their gods, washing them with lotus-scented water and oiling them before dressing the statue with jewelry, clothes, and make-up.
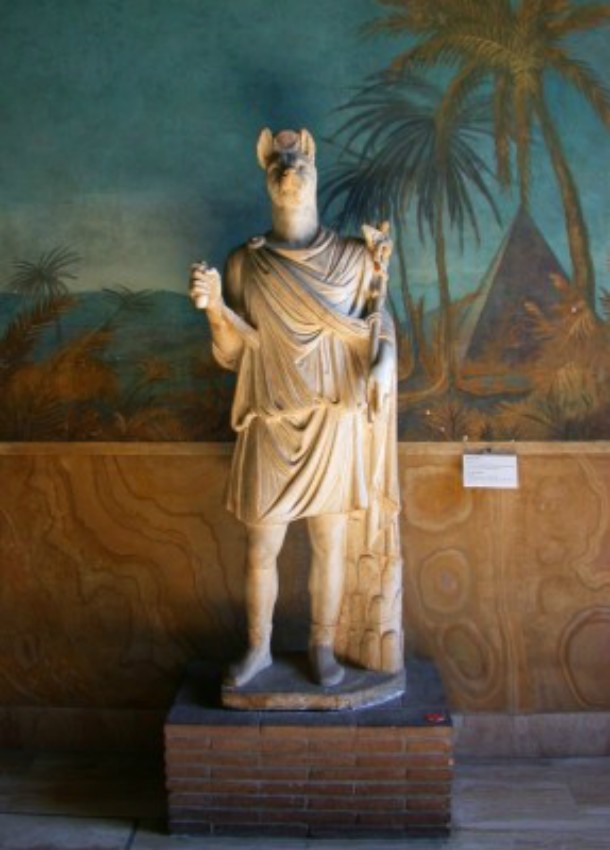 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia One of the most hated Egyptian gods, Set (on the left) was the god of chaos, confusion, and war. He has a human body but an animal head which Egyptologists have been unable to identify with any known animal. Set was specifically hated for murdering his brother Osiris and taking over the throne.
 Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia
Source: Discovering Egypt, Image: Wikipedia One of the most distinctive signs of Ancient Egypt, the Eye of Horus was often worn as a protective amulet. It represents healing and restoration and was believed to protect its wearer with good magic. Various symbols have been based on the Eye of Horus, including the all-seeing eye in the United States' Great Seal on the dollar bill and the Rx symbol in pharmacy.
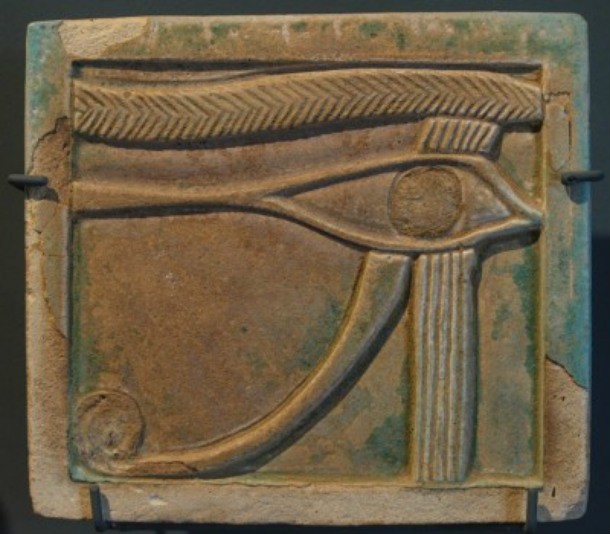 Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia
Source: Land of Pyramids, Image: Wikimedia 


























