Ever thought about how your body manages to digest the food you consume? It might be hard to believe, but the digestive system is incredibly sophisticated with many functioning components. Naturally, without it, there would be no way for you to get energy or continue living.
However, it also clears waste and filters out toxins. It’s an indispensable part of your body, so why not learn more about it? Here are 25 Fun Facts About The Human Digestive System You Probably Didn’t Know.

Food takes about seven seconds to travel down the esophagus.
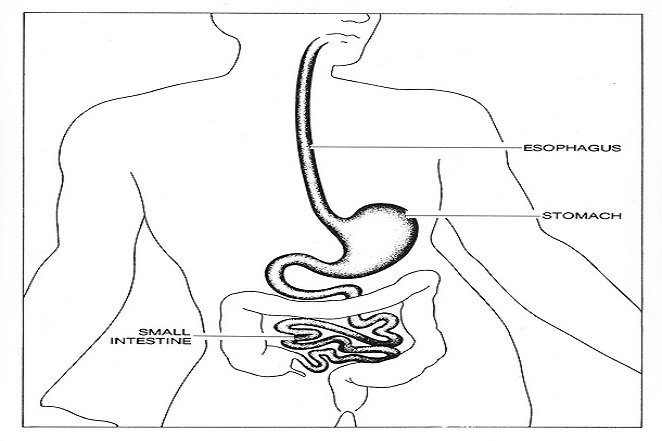 Source: http://www.wisegeek.com
Source: http://www.wisegeek.com The small intestine is 22 feet long, while the large intestine is only 6 feet.
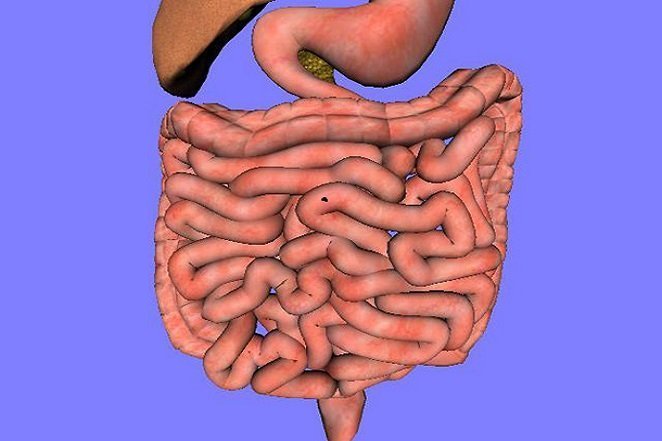 Source: https://www.livescience.com
Source: https://www.livescience.com The entire digestive system from the mouth to the anus is 30 feet long.
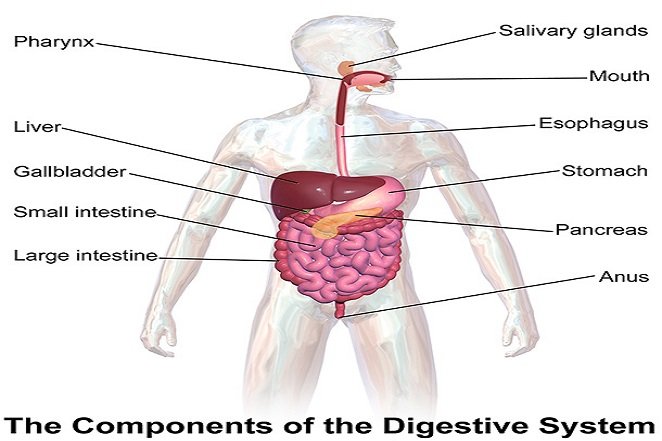 Source: http://www.newsmax.com
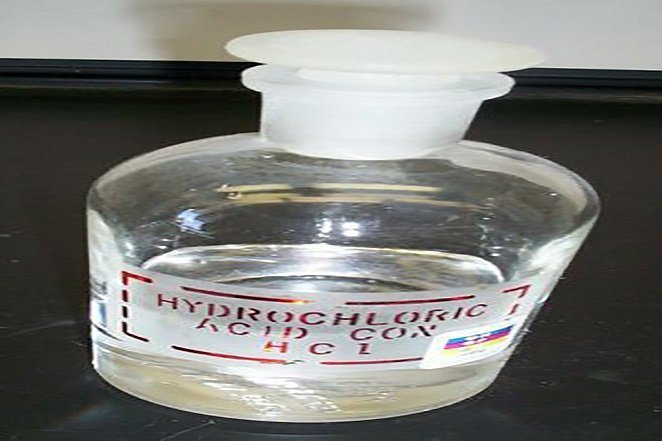
Source: http://www.newsmax.com Your stomach uses hydrochloric acid to break down food and produces a mucus to protect itself from it.
 Source: http://health.howstuffworks.com
Source: http://health.howstuffworks.com The small intestine has three parts: the Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum.
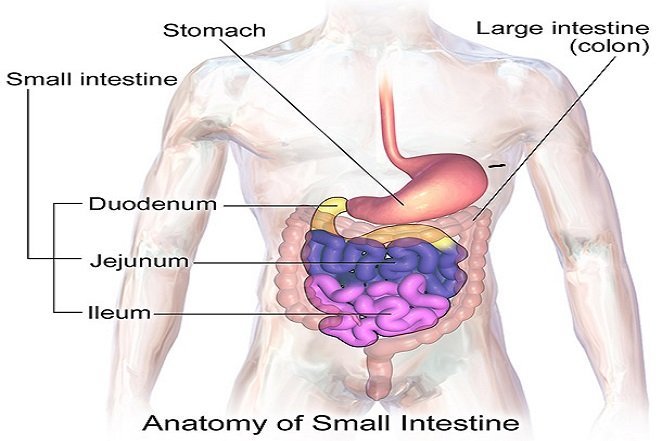 Source: http://www.webmd.com
Source: http://www.webmd.com An adult's stomach can hold about 1.5 liters of material.
 Source: http://warriors.warren.k12.il.us/
Source: http://warriors.warren.k12.il.us/ Contrary to popular belief, the small intestine is where most of digestion takes place, not the stomach.
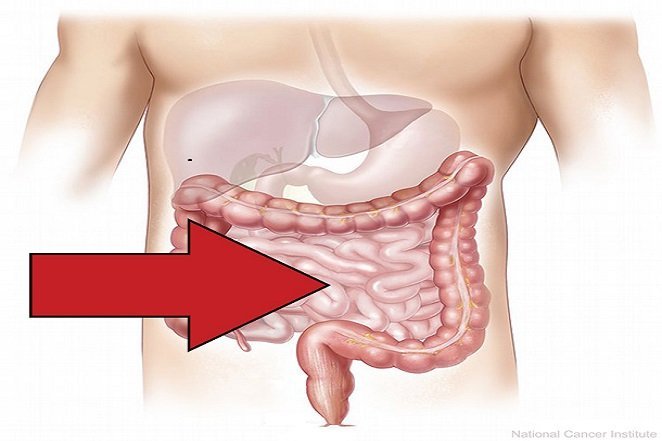 Source: https://www.diet.com
Source: https://www.diet.com Your stomach growling is called "borborygmi," and it's actually your intestines full of hot air.
 Source: http://www.webmd.com/
Source: http://www.webmd.com/ Our salivary glands produce 1 to 2 liters of saliva a day.
 Source: https://www.livescience.com
Source: https://www.livescience.com Your gut and brain have a special connection. Emotions, like anger, anxiety, and sadness, can change how you digest food.
 Source: https://www.health.harvard.edu
Source: https://www.health.harvard.edu Enzymes in your stomach aid in breaking food down into proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
 Source: https://nationalenzyme.com
Source: https://nationalenzyme.com Peptic ulcers are not caused by stress or diet but by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori.
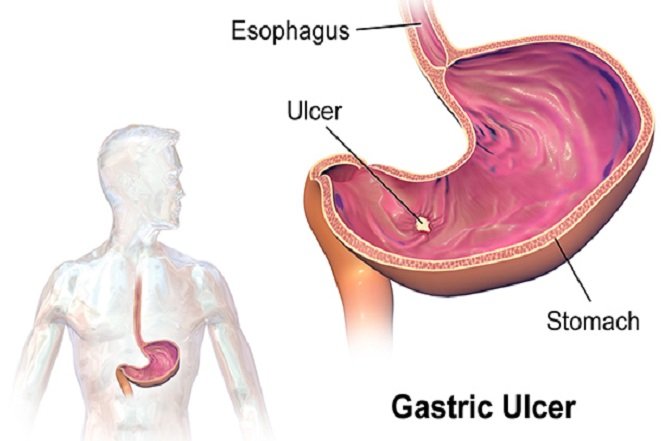 Source: https://www.cdc.gov/ulcer/history.htm
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/ulcer/history.htm The average American adult eats roughly 2,000 lbs of food a year.
 Source: https://www.niftyhomestead.com
Source: https://www.niftyhomestead.com Belching is a result of sucking in excess air while drinking a carbonated beverage, chewing gum, or smoking.
 Source: http://www.mayoclinic.org
Source: http://www.mayoclinic.org The colon has four major parts and is responsible for getting rid of food after the nutrients are removed.
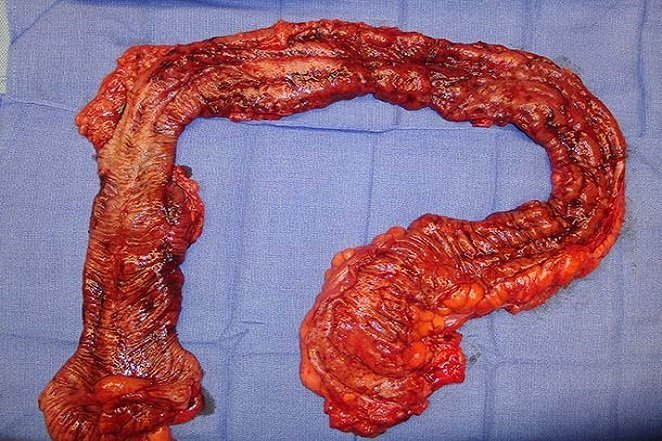 Source: https://www.livescience.com
Source: https://www.livescience.com The esophagus moves food down to the stomach using muscles in a process called peristalsis.
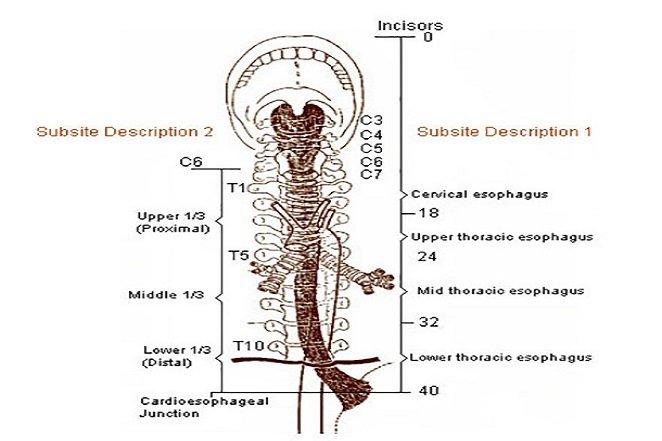 Source: http://www.nyp.org/
Source: http://www.nyp.org/ The liver is the largest internal organ and has over 500 different functions including fighting off infection and neutralizing toxins.
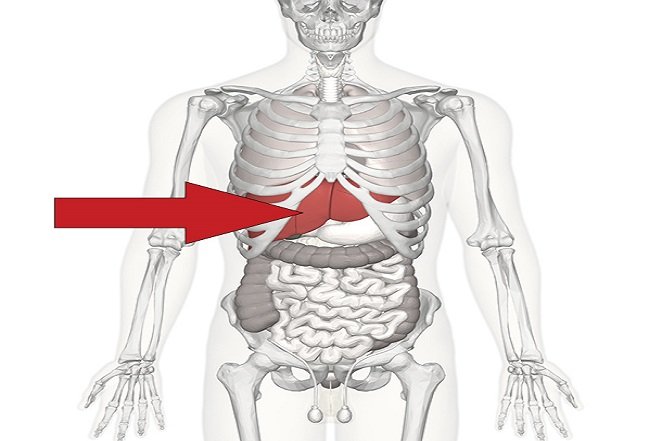 Source: http://www.liver.ca
Source: http://www.liver.ca The human digestive system doesn't rely on gravity since food is moved through using muscles. This means you could be standing on your head and your digestive system would keep working. However, we can't promise that doing a headstand right after eating would be entirely comfortable.
 Source: dailyhealthpost.com
Source: dailyhealthpost.com In 1822, a fur trapper suffered a horrible gun shot wound in the stomach. After several surgeries, he survived, but they had to keep the hole, providing a window for doctors to watch digestion in real time.
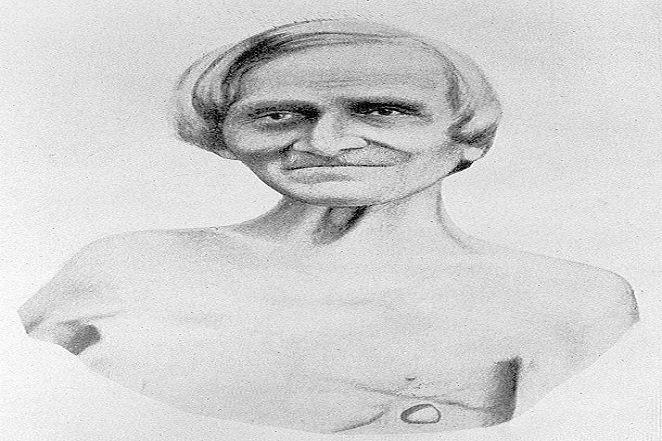 Source: https://www.livescience.com
Source: https://www.livescience.com Flatulence is essentially swallowed air and gas produced by bacteria in your intestines.

The human gut is home to a complex ecosystem of roughly 300 to 500 bacteria.
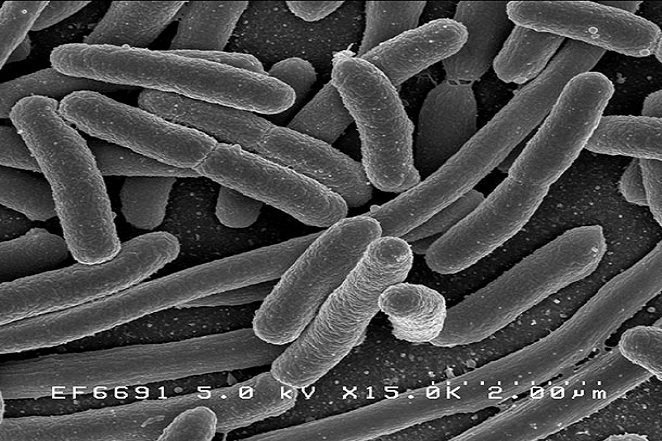 Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ The entire intestinal tract is sterile at birth and is populated by environmental factors during and after birth.
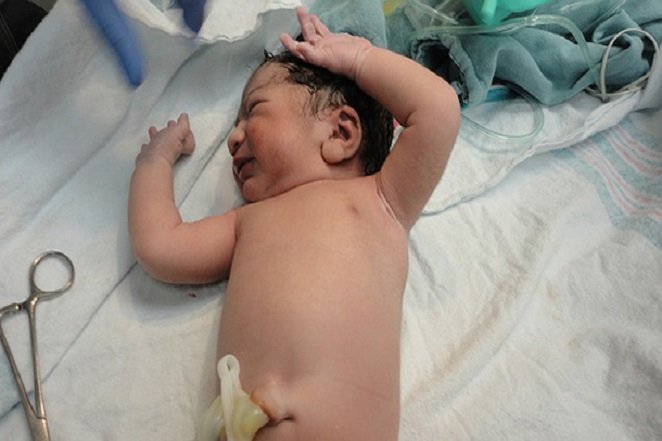 Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ To prevent food and liquid from entering your lungs, the epiglottis covers the entrance to the larynx.
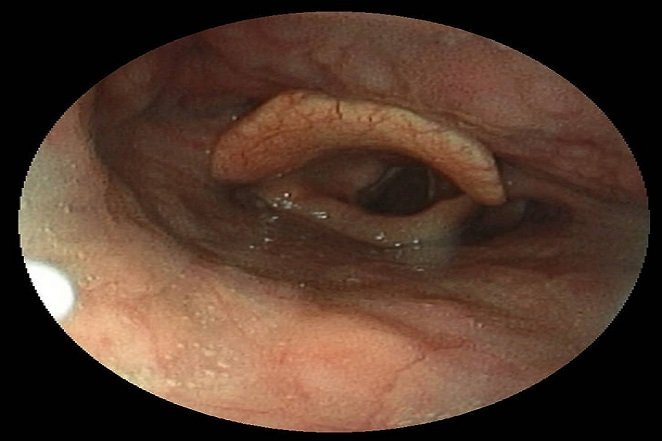 Source: http://www.livestrong.com/
Source: http://www.livestrong.com/ The gallbladder stores the bile used to break down dietary fat.
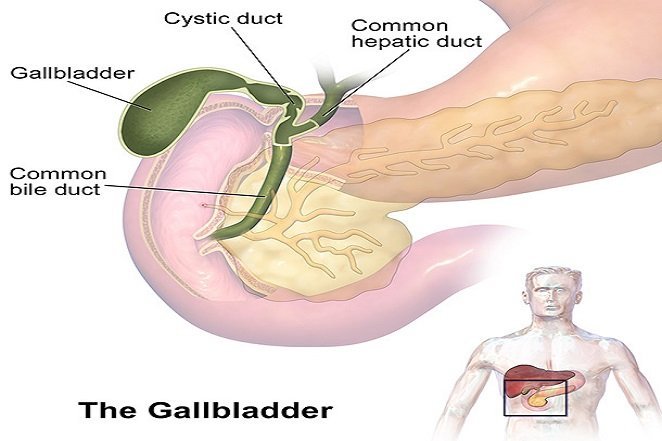 Source: http://www.sciencekids.co.nz
Source: http://www.sciencekids.co.nz The digestive system is the site of more cancers and cancer moratlity than any other in the body.
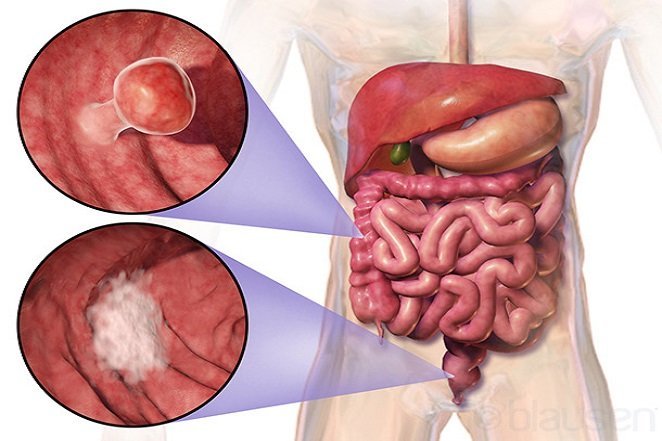 Source: https://www.niddk.nih.gov
Source: https://www.niddk.nih.gov Lists Going Viral Right Now
Photo: feature: shutterstock, 25. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 24. LearnAnatomy (talk), DH small intestine, CC BY 3.0, 23. BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources it can be cited as: Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014“. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436., Blausen 0316 DigestiveSystem, CC BY 3.0, 22. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 21. BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources it can be cited as: Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014“”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436., Blausen 0817 SmallIntestine Anatomy, CC BY 3.0, 20. FatGiVi, Obese teenagers male overweight fat front belly, CC BY-SA 4.0, 19. The original uploader was Arnavaz at French Wikipedia This image is an old version created by Medium69. Cette image est une ancienne version créée par Medium69. Please credit this : William Crochot , Digestive appareil (dumb version), CC BY-SA 4.0, 18. shutterstock, 17. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 16. Pixabay.com (Public Domain), 15. BruceBlaus, Gastric Ulcer, CC BY-SA 4.0, 14. Love Food Hate Waste NZ, 42.4 kg of food found in New Zealand household rubbish bins, CC BY-SA 4.0, 13. Neil Rogers via flickr., 12. Theron Price, Human Colon, Removed Feb 2010, Condition Ulcerative Colitis, CC BY-SA 3.0, 11. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 10. Polygon data is generated by Database Center for Life Science(DBCLS)[2], Liver 01 anterior view, CC BY-SA 1.0, 9. WIkipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 8. pixabay (public domain), 7. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 6. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 5. Wikipedia Commons.com (Public Domain), 4. Pixabay.com (Public Domain), 3. Med Chaos, Normal Epiglottis, CC BY-SA 3.0, 2. BruceBlaus, Gallbladder (organ), CC BY-SA 4.0, 1. Blausen Medical Communications, Inc., Blausen 0246 ColorectalCancer, CC BY 3.0



























